Carvacrol inhibits the progression of oral submucous fibrosis via downregulation of PVT1/miR-20a-5p-mediated pyroptosis
- PMID: 39320020
- PMCID: PMC11423347
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70112
Carvacrol inhibits the progression of oral submucous fibrosis via downregulation of PVT1/miR-20a-5p-mediated pyroptosis
Abstract
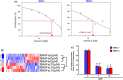
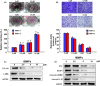
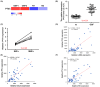
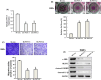
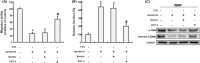
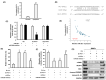
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) is a precancerous condition in the oral cavity, which is closely related to the myofibroblast conversion of buccal mucosal fibroblasts (BMFs) after chronic consumption of areca nut. Emerging evidence suggests pyroptosis, a form of programmed cell death that is mediated by inflammasome, is implicated in persistent myofibroblast activation and fibrosis. Besides, numerous studies have demonstrated the effects of non-coding RNAs on pyroptosis and myofibroblast activities. Herein, we aimed to target key long non-coding RNA PVT1 with natural compound, carvacrol, to alleviate pyroptosis and myofibroblast activation in OSF. We first identified PVT1 was downregulated in the carvacrol-treated fBMFs and then demonstrated that myofibroblast features and expression of pyroptosis makers were all reduced in response to carvacrol treatment. Subsequently, we analysed the expression of PVT1 and found that PVT1 was aberrantly upregulated in OSF specimens and positively correlated with several fibrosis markers. After revealing the suppressive effects of carvacrol on myofibroblast characterisitcs and pyroptosis were mediated by repression of PVT1, we then explored the potential mechanisms. Our data showed that PVT1 may serve as a sponge of microRNA(miR)-20a to mitigate the myofibroblast activation and pyroptosis. Altogether, these findings indicated that the anti-fibrosis effects of carvacrol merit consideration and may be due to the attenuation of pyroptosis and myofibroblast activation by targeting the PVT1/miR-20a axis.
Keywords: PVT1; carvacrol; microRNA‐20a; myofibroblast; oral submucous fibrosis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-200b ameliorates myofibroblast transdifferentiation in precancerous oral submucous fibrosis through targeting ZEB2.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Sep;22(9):4130-4138. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13690. Epub 2018 Jun 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29893466 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting lncRNA H19/miR-29b/COL1A1 Axis Impedes Myofibroblast Activities of Precancerous Oral Submucous Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 23;22(4):2216. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042216. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672311 Free PMC article.
-
MIAT promotes myofibroblastic activities and transformation in oral submucous fibrosis through sponging the miR-342-3p/SOX6 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Oct 7;16(19):12909-12927. doi: 10.18632/aging.206121. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39379100 Free PMC article.
-
The functional roles of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis.J Dent Sci. 2022 Apr;17(2):683-687. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.07.008. Epub 2021 Aug 1. J Dent Sci. 2022. PMID: 35756801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myofibroblasts persist through immune privilege mechanisms to mediate oral submucous fibrosis: Uncovering the pathogenesis.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024 Nov-Dec;14(6):773-781. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.10.008. Epub 2024 Oct 20. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 39502133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

