Population Structure and Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli Isolated from Humans with Diarrhea and from Poultry, East Africa
- PMID: 39320160
- PMCID: PMC11431929
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3010.231399
Population Structure and Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli Isolated from Humans with Diarrhea and from Poultry, East Africa
Abstract
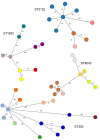
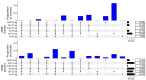
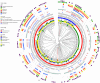
Campylobacteriosis and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are global public health concerns. Africa is estimated to have the world's highest incidence of campylobacteriosis and a relatively high prevalence of AMR in Campylobacter spp. from humans and animals. Few studies have compared Campylobacter spp. isolated from humans and poultry in Africa using whole-genome sequencing and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. We explored the population structure and AMR of 178 Campylobacter isolates from East Africa, 81 from patients with diarrhea in Kenya and 97 from 56 poultry samples in Tanzania, collected during 2006-2017. Sequence type diversity was high in both poultry and human isolates, with some sequence types in common. The estimated prevalence of multidrug resistance, defined as resistance to >3 antimicrobial classes, was higher in poultry isolates (40.9%, 95% credible interval 23.6%-59.4%) than in human isolates (2.5%, 95% credible interval 0.3%-6.8%), underlining the importance of antimicrobial stewardship in livestock systems.
Keywords: Campylobacter coli; Campylobacter jejuni; Kenya; Tanzania; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; campylobacteriosis; east Africa; enteric infections; humans; poultry; zoonoses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Campylobacter species prevalence, characterisation of antimicrobial resistance and analysis of whole-genome sequence of isolates from livestock and humans, Latvia, 2008 to 2016.Euro Surveill. 2019 Aug;24(31):1800357. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.31.1800357. Euro Surveill. 2019. PMID: 31387670 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, antibiotic resistance and genotypes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from chickens in Irbid governorate, Jordan.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Aug 16;327:108656. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108656. Epub 2020 May 11. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32445835
-
Sharing of cmeRABC alleles between C. coli and C. jejuni associated with extensive drug resistance in Campylobacter isolates from infants and poultry in the Peruvian Amazon.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0205424. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02054-24. Epub 2024 Dec 27. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39727415 Free PMC article.
-
The Current State of Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter spp.: Trends and Impacts of Resistance Mechanisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 May 31;83(12):e00416-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00416-17. Print 2017 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28411226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial resistance in selected bacteria from poultry.Anim Health Res Rev. 2008 Dec;9(2):149-58. doi: 10.1017/S1466252308001552. Anim Health Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 19102788 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of Campylobacter species diversity in infants and association with family members, livestock, and household environments in rural Eastern Ethiopia.Gut Pathog. 2025 Jul 5;17(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00725-0. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40618155 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission pathways of Campylobacter jejuni between humans and livestock in rural Ethiopia are highly complex and interdependent.Gut Pathog. 2025 May 3;17(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00691-7. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40319305 Free PMC article.
-
The Global Challenge of Campylobacter: Antimicrobial Resistance and Emerging Intervention Strategies.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 16;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed10010025. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39852676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Campylobacter Lineages in New Zealand Freshwater: Pathogenesis and Public Health Implications.Environ Microbiol. 2024 Dec;26(12):e70016. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.70016. Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39680962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirk MD, Pires SM, Black RE, Caipo M, Crump JA, Devleesschauwer B, et al. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001921. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001921 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amour C, Gratz J, Mduma E, Svensen E, Rogawski ET, McGrath M, et al. ; Etiology, Risk Factors, and Interactions of Enteric Infections and Malnutrition and the Consequences for Child Health and Development Project (MAL-ED) Network Investigators. Epidemiology and Impact of Campylobacter Infection in Children in 8 Low-Resource Settings: Results From the MAL-ED Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:1171–9. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

