Correlation between Viral Wastewater Concentration and Respiratory Tests, Oregon, USA
- PMID: 39320239
- PMCID: PMC11431916
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3010.240637
Correlation between Viral Wastewater Concentration and Respiratory Tests, Oregon, USA
Abstract
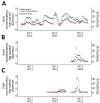
We evaluated the association between wastewater concentration and weekly percent positivity of patient testing for SARS-CoV-2, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus in Oregon, USA. We found strong, positive correlations for SARS-CoV-2 (ρ = 0.84, p<0.001), influenza (ρ = 0.73, p<0.001) and respiratory syncytial virus (ρ = 0.69, p<0.001).
Keywords: COVID-19; Oregon; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; correlation study; environmental surveillance; influenza; respiratory syncytial virus; viruses; wastewater surveillance; wastewater-based epidemiology.
Figures
References
-
- Hopkins L, Persse D, Caton K, Ensor K, Schneider R, McCall C, et al. Citywide wastewater SARS-CoV-2 levels strongly correlated with multiple disease surveillance indicators and outcomes over three COVID-19 waves. Sci Total Environ. 2023;855:158967. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158967 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acosta N, Bautista MA, Waddell BJ, McCalder J, Beaudet AB, Man L, et al. Longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 RNA wastewater monitoring across a range of scales correlates with total and regional COVID-19 burden in a well-defined urban population. Water Res. 2022;220:118611. 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118611 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehm AB, Hughes B, Duong D, Chan-Herur V, Buchman A, Wolfe MK, et al. Wastewater concentrations of human influenza, metapneumovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, and seasonal coronavirus nucleic-acids during the COVID-19 pandemic: a surveillance study. Lancet Microbe. 2023;4:e340–8. 10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00386-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

