Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prevalence and Risk Factors among Healthy Term Infants, United States
- PMID: 39320243
- PMCID: PMC11431910
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3010.240609
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prevalence and Risk Factors among Healthy Term Infants, United States
Abstract
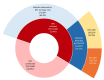
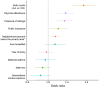
In a population-based birth cohort study of respiratory syncytial virus surveillance in the United States, 897/1,680 (53.4%) children were infected during infancy; 25 (2.8%) of those were hospitalized. Among symptomatic infants, 143/324 (44.1%) had lower respiratory tract infections. These data provide benchmarks to monitor effects of maternal vaccines and extended half-life monoclonal antibodies.
Keywords: RSV; United States; infant; respiratory infections; respiratory syncytial virus; risk factors; viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Li Y, Wang X, Blau DM, Caballero MT, Feikin DR, Gill CJ, et al. ; Respiratory Virus Global Epidemiology Network; RESCEU investigators. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399:2047–64. 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00478-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Larkin EK, Gebretsadik T, Moore ML, Anderson LJ, Dupont WD, Chappell JD, et al. ; INSPIRE Study. Objectives, design, and enrollment results from the Infant Susceptibility to Pulmonary Infections and Asthma Following RSV Exposure Study (INSPIRE). BMC Pulm Med. 2015;15:45. 10.1186/s12890-015-0040-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosas-Salazar C, Chirkova T, Gebretsadik T, Chappell JD, Peebles RS Jr, Dupont WD, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus infection during infancy and asthma during childhood in the USA (INSPIRE): a population-based, prospective birth cohort study. Lancet. 2023;401:1669–80. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00811-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

