Automatic Segmentation of Ultrasound-Guided Quadratus Lumborum Blocks Based on Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 39320548
- PMCID: PMC12092921
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01267-8
Automatic Segmentation of Ultrasound-Guided Quadratus Lumborum Blocks Based on Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
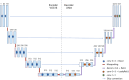
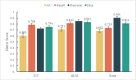
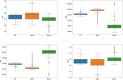
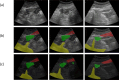
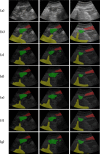
Ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block (QLB) technology has become a widely used perioperative analgesia method during abdominal and pelvic surgeries. Due to the anatomical complexity and individual variability of the quadratus lumborum muscle (QLM) on ultrasound images, nerve blocks heavily rely on anesthesiologist experience. Therefore, using artificial intelligence (AI) to identify different tissue regions in ultrasound images is crucial. In our study, we retrospectively collected 112 patients (3162 images) and developed a deep learning model named Q-VUM, which is a U-shaped network based on the Visual Geometry Group 16 (VGG16) network. Q-VUM precisely segments various tissues, including the QLM, the external oblique muscle, the internal oblique muscle, the transversus abdominis muscle (collectively referred to as the EIT), and the bones. Furthermore, we evaluated Q-VUM. Our model demonstrated robust performance, achieving mean intersection over union (mIoU), mean pixel accuracy, dice coefficient, and accuracy values of 0.734, 0.829, 0.841, and 0.944, respectively. The IoU, recall, precision, and dice coefficient achieved for the QLM were 0.711, 0.813, 0.850, and 0.831, respectively. Additionally, the Q-VUM predictions showed that 85% of the pixels in the blocked area fell within the actual blocked area. Finally, our model exhibited stronger segmentation performance than did the common deep learning segmentation networks (0.734 vs. 0.720 and 0.720, respectively). In summary, we proposed a model named Q-VUM that can accurately identify the anatomical structure of the quadratus lumborum in real time. This model aids anesthesiologists in precisely locating the nerve block site, thereby reducing potential complications and enhancing the effectiveness of nerve block procedures.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Image segmentation; Quadratus lumborum block; Ultrasonography.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Peking Union Medical College under approval number 23/139–3891. Consent to Participate: Written informed consent was obtained from the parents. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Jin Z, Liu J, Li R, et al. Single injection quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia in adult surgical population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Anesth 62:109715, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Saranteas T, Koliantzaki I, Savvidou O, et al. Acute pain management in trauma: anatomy, ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks and special considerations. Minerva Anestesiol 85:763-773, 2019. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 7232133/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
- 2022-I2M-C&T-B-086/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- LC2022A05/Beijing Hope Run Special Fund of the Cancer Foundation of China
- 2023QNRC001/Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program of CAST
- 2021YFA1301603/Key Technologies Research and Development Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
