Aspertaichamide B, a new anti-tumor prenylated indole alkaloid from the fungus Aspergillus japonicus TE-739D
- PMID: 39320549
- PMCID: PMC11424712
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-024-13313-0
Aspertaichamide B, a new anti-tumor prenylated indole alkaloid from the fungus Aspergillus japonicus TE-739D
Abstract
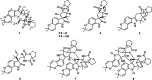
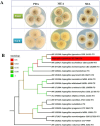
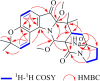
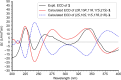
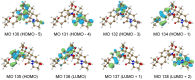
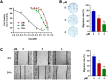
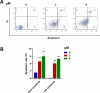
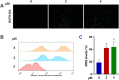
Prenylated indole alkaloids, which are mainly produced by genera Aspergillus and Penicillium, are a class of structurally intriguing specialized metabolites with remarkable biomedical interests. In this study, chemically guided isolation of the Nicotiana tabacum-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus japonicus TE-739D yielded eight structurally diverse prenylated indole alkaloids, including an undescribed compound, namely aspertaichamide B (ATB, 1), together with seven previously discovered derivatives (compounds 2 - 8). Their chemical structures as well as the stereochemical features were determined by integrated spectroscopic analyses, including HRESIMS, NMR, NMR calculations with DP4 + probability analysis, and a comparison of the experimental ECD data with computed DFT-based quantum chemical calculations. In vitro cytotoxic effects against the gastric cancer MFC cells revealed that the new compound ATB demonstrated considerable activity. Further studies found that ATB suppressed the viability, colony formation, and migration ability of MFC cells, and induced MFC cells apoptosis in a concentration-dependent way. Moreover, ATB stimulated ROS production in MFC cells and inhibited the tumor growth in the MFC-sourced subcutaneous tumor model while not significantly reducing the weight of mice. The pharmacological results suggested that the newly discovered ATB may be a promising anti-tumor lead compound. KEY POINTS: • Eight structurally diverse prenylated indole alkaloids including a new aspertaichamide B (ATB) were isolated from the fungus Aspergillus japonicus TE-739D. • The structure of ATB was elucidated by HRESIMS, NMR, NMR calculations with DP4 + probability analysis, and ECD calculations. • ATB inhibited cell proliferation, promoted apoptosis, and increased ROS production in gastric cancer cells, and exhibited inhibitory effects on tumor growth in vivo.
Keywords: Aspergillus japonicus; Anti-tumor activity; Endophytic fungus; Prenylated indole alkaloids; Specialized metabolites.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspertaichamide a, a novel cytotoxic prenylated indole alkaloid possessing a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane framework from a marine algal-derived endophytic fungus aspergillus taichungensis 299.Fitoterapia. 2024 Jan;172:105763. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105763. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Fitoterapia. 2024. PMID: 38040094
-
Versicoamides F-H, Prenylated Indole Alkaloids from Aspergillus tennesseensis.Org Lett. 2017 Feb 17;19(4):942-945. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00145. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Org Lett. 2017. PMID: 28181808
-
Prenylated indole diketopiperazine alkaloids as phosphatase inhibitors from the marine-derived fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus.Phytochemistry. 2024 Jul;223:114119. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2024.114119. Epub 2024 May 3. Phytochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38705266
-
Structural and stereochemical diversity in prenylated indole alkaloids containing the bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane ring system from marine and terrestrial fungi.Nat Prod Rep. 2018 Jun 20;35(6):532-558. doi: 10.1039/c7np00042a. Nat Prod Rep. 2018. PMID: 29632911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenylated indole derivatives from fungi: structure diversity, biological activities, biosynthesis and chemoenzymatic synthesis.Nat Prod Rep. 2010 Jan;27(1):57-78. doi: 10.1039/b909987p. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Nat Prod Rep. 2010. PMID: 20024094 Review.
References
-
- Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A, Donato R (2018) Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta-Mol Cell Res 1865:721–733 - PubMed
-
- Chandra S (2012) Endophytic fungi: novel sources of anticancer lead molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:47–59 - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Wang SP, Xu LC, Liang C, Liu GD, Ji X, Luo WH, Liu S, Zhang ZX, Cao GY (2024) Aspertaichamide a, a novel cytotoxic prenylated indole alkaloid possessing a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane framework from a marine algal-derived endophytic fungus aspergillus taichungensis 299. Fitoterapia 172:105763 - PubMed
-
- DeNicola GM, Karreth FA, Humpton TJ, Gopinathan A, Wei C, Frese K, Mangal D, Yu KH, Yeo CJ, Calhoun ES, Scrimieri F, Winter JM, Hruban RH, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Kern S, Blair IA, Tuveson DA (2011) Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 475:106–109 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding Y, de Wet JR, Cavalcoli J, Li S, Greshock TJ, Miller KA, Finefield JM, Sunderhaus JD, McAfoos TJ, Tsukamoto S, Williams RM, Sherman DH (2010) Genome-based characterization of two prenylation steps in the assembly of the stephacidin and notoamide anticancer agents in a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. J Am Chem Soc 132:12733–12740 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

