Epigenetic tuning of tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs): a potential approach in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immunotherapy
- PMID: 39320855
- PMCID: PMC11440614
- DOI: 10.1017/erm.2024.9
Epigenetic tuning of tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs): a potential approach in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immunotherapy
Abstract
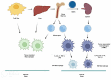
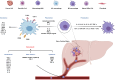
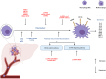
Recent development in immunotherapy for cancer treatment has substantiated to be more effective than most of the other treatments. Immunity is the first line of defence of the body; nevertheless, cancerous cells can manipulate immunity compartments to play several roles in tumour progression. Tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs), one of the most dominant components in the tumour microenvironment, are recognized as anti-tumour suppressors. Unfortunately, the complete behaviour of TAMs is still unclear and understudied. TAM density is directly correlated with the progression and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), therefore studying TAMs from different points of view passing by all the factors that may affect its existence, polarization, functions and repolarization are of great importance. Different epigenetic regulations were reported to have a direct relation with both HCC and TAMs. Here, this review discusses different epigenetic regulations that can affect TAMs in HCC whether positively or negatively.
Keywords: epigenetics; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); immunotherapy; macrophages; tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: impact, mechanism, and therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1429812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429812. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor‑associated macrophages activated in the tumor environment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Characterization and treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Oct;65(4):100. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5688. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39239752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FABP5+ lipid-loaded macrophages process tumour-derived unsaturated fatty acid signal to suppress T-cell antitumour immunity.J Hepatol. 2025 Apr;82(4):676-689. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.09.029. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39357545
-
Preferential Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 Protein in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Its Potential Role in Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4710. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094710. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946835 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages as Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Jun 4;23(6):780-790. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-23-0660. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38310642 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Mar 21;20(1):20241117. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1117. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40129528 Free PMC article.
-
MIAT: A pivotal oncogenic long noncoding RNA tunning the hallmarks of solid malignancies.Transl Oncol. 2025 Apr;54:102329. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102329. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40014977 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing myeloid cells in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2025 Mar 6;24(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02249-2. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40050933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Burden of Cancer, The Cancer Atlas. Available at https://canceratlas.cancer.org/the-burden/the-burden-of-cancer/
-
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Practice essentials, anatomy, pathophysiology. Available at https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/197319-overview
-
- Types, Liver Cancer, Cancer Research UK. Available at https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/liver-cancer/types
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

