Decreased PU.1 expression in mature B cells induces lymphomagenesis
- PMID: 39321027
- PMCID: PMC11611758
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16344
Decreased PU.1 expression in mature B cells induces lymphomagenesis
Abstract
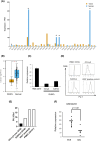
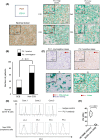
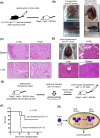
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of lymphoma, accounting for 30% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Although comprehensive analysis of genetic abnormalities has led to the classification of lymphomas, the exact mechanism of lymphomagenesis remains elusive. The Ets family transcription factor, PU.1, encoded by Spi1, is essential for the development of myeloid and lymphoid cells. Our previous research illustrated the tumor suppressor function of PU.1 in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and myeloma cells. In the current study, we found that patients with DLBCL exhibited notably reduced PU.1 expression in their lymphoma cells, particularly in the non-germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) subtype. This observation suggests that downregulation of PU.1 may be implicated in DLBCL tumor growth. To further assess PU.1's role in mature B cells in vivo, we generated conditional Spi1 knockout mice using Cγ1-Cre mice. Remarkably, 13 of the 23 knockout mice (56%) showed splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, or masses, with some having histologically confirmed B-cell lymphomas. In contrast, no wild-type mice developed B-cell lymphoma. In addition, RNA-seq analysis of lymphoma cells from Cγ1-Cre Spi1F/F mice showed high frequency of each monoclonal CDR3 sequence, indicating that these lymphoma cells were monoclonal tumor cells. When these B lymphoma cells were transplanted into immunodeficient recipient mice, all mice died within 3 weeks. Lentiviral-transduced Spi1 rescued 60% of the recipient mice, suggesting that PU.1 has a tumor suppressor function in vivo. Collectively, PU.1 is a tumor suppressor in mature B cells, and decreased PU.1 results in mature B-cell lymphoma development.
Keywords: DLBCL; PU.1; Spi1; diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; lymphomagenesis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Koichi Akashi, Masao Matsuoka, and Yoshihiro Komohara are editorial board members of
Figures



References
-
- Pfreundschuh M, Trümper L, Osterborg A, et al. CHOP‐like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP‐like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good‐prognosis diffuse large‐B‐cell lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) group. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(5):379‐391. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70664-7 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

