WDR5 Binding to Histone Serotonylation Is Driven by an Edge-Face Aromatic Interaction with Unexpected Electrostatic Effects
- PMID: 39321462
- PMCID: PMC12132056
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c07277
WDR5 Binding to Histone Serotonylation Is Driven by an Edge-Face Aromatic Interaction with Unexpected Electrostatic Effects
Abstract
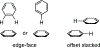
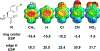
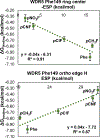
Histone serotonylation has emerged as a key post-translational modification. WDR5 preferentially binds to serotonylated histone 3 (H3), and this binding event has been associated with tumorigenesis. Herein, we utilize genetic code expansion, structure-activity relationship studies, and computation to study an edge-face aromatic interaction between WDR5 Phe149 and serotonin on H3 that is key to this protein-protein interaction. We find experimentally that this edge-face aromatic interaction is unaffected by modulating the electrostatics of the face component but is weakened by electron-withdrawing substituents on the edge component. Overall, these results elucidate that this interaction is governed by van der Waals forces as well as electrostatics of the edge ring, a result that clarifies discrepancies among previous theoretical models and model system studies of this interaction type. This is the first evaluation of the driving force of an edge-face aromatic interaction at a protein-protein interface and provides a key benchmark for the nature of these understudied interactions that are abundant in the proteome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


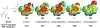
References
-
- Couture J-F; Collazo E; Trievel RC, Molecular recognition of histone H3 by the WD40 protein WDR5. Nature structural & molecular biology 2006, 13 (8), 698–703. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

