Sirolimus reduces T cell cycling, immune checkpoint marker expression, and HIV-1 DNA in people with HIV
- PMID: 39321793
- PMCID: PMC11513808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101745
Sirolimus reduces T cell cycling, immune checkpoint marker expression, and HIV-1 DNA in people with HIV
Abstract
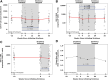
Key HIV cure strategies involve reversing immune dysfunction and limiting the proliferation of infected T cells. We evaluate the safety of sirolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor, in people with HIV (PWH) and study the impact of sirolimus on HIV-1 reservoir size and HIV-1-specific immunity in a single-arm study of 20 weeks of treatment in PWH on antiretroviral therapy (ART). Sirolimus treatment does not impact HIV-1-specific CD8 T cell responses but leads to a significant decrease in CD4+ T cell-associated HIV-1 DNA levels at 20 weeks of therapy in the primary efficacy population (n = 16; 31% decline, p = 0.008). This decline persists for at least 12 weeks following cessation of the study drug. Sirolimus treatment also leads to a significant reduction in CD4+ T cell cycling and PD-1 expression on CD8+ lymphocytes. These data suggest that homeostatic proliferation of infected cells, an important mechanism for HIV persistence, is an intriguing therapeutic target.
Keywords: HIV curative strategies; HIV immunology; HIV persistence; HIV reservoirs; HIV-1; antiproliferative medications; immunotherapy; intact proviral HIV-1 DNA; mTOR inhibition; sirolimus.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.J.H. received grant support from Gilead Sciences, Merck, and Bristol Myers Squibb. D.R.K. receives grant support and/or consulting honoraria from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Roche, and ViiV. J.Z.L. received grant support from Merck.
Figures



References
-
- International AIDS Society Scientific Working Group on HIV Cure. Deeks S.G., Autran B., Berkhout B., Benkirane M., Cairns S., Chomont N., Chun T.W., Churchill M., Di Mascio M., et al. Towards an HIV cure: a global scientific strategy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012;12:607–614. doi: 10.1038/nri3262. nri3262 [pii] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deeks S.G., Archin N., Cannon P., Collins S., Jones R.B., de Jong M.A.W.P., Lambotte O., Lamplough R., Ndung'u T., Sugarman J., et al. Research priorities for an HIV cure: International AIDS Society Global Scientific Strategy 2021. Nat. Med. 2021;27:2085–2098. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01590-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

