Combining systems and synthetic biology for in vivo enzymology
- PMID: 39322757
- PMCID: PMC11535393
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00251-w
Combining systems and synthetic biology for in vivo enzymology
Abstract
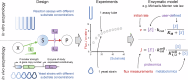
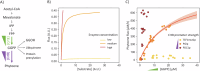
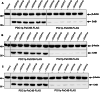
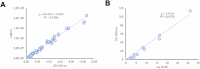
Enzymatic parameters are classically determined in vitro, under conditions that are far from those encountered in cells, casting doubt on their physiological relevance. We developed a generic approach combining tools from synthetic and systems biology to measure enzymatic parameters in vivo. In the context of a synthetic carotenoid pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we focused on a phytoene synthase and three phytoene desaturases, which are difficult to study in vitro. We designed, built, and analyzed a collection of yeast strains mimicking substantial variations in substrate concentration by strategically manipulating the expression of geranyl-geranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthase. We successfully determined in vivo Michaelis-Menten parameters (KM, Vmax, and kcat) for GGPP-converting phytoene synthase from absolute metabolomics, fluxomics and proteomics data, highlighting differences between in vivo and in vitro parameters. Leveraging the versatility of the same set of strains, we then extracted enzymatic parameters for two of the three phytoene desaturases. Our approach demonstrates the feasibility of assessing enzymatic parameters directly in vivo, providing a novel perspective on the kinetic characteristics of enzymes in real cellular conditions.
Keywords: Biotechnology; Carotenoid Synthesis; Enzymatic Parameters; In Vivo vs In Vitro; Metabolism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bruggeman FJ, Hornberg JJ, Boogerd FC, Westerhoff HV (2007) Introduction to systems biology. EXS 97:1–19 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

