Tissue-specific functions of MSCs are linked to homeostatic muscle maintenance and alter with aging
- PMID: 39323233
- PMCID: PMC11561651
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14299
Tissue-specific functions of MSCs are linked to homeostatic muscle maintenance and alter with aging
Abstract
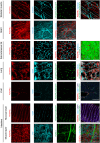
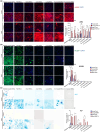
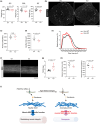
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), also known as fibro-adipogenic progenitors, play a critical role in muscle maintenance and sarcopenia development. Although analogous MSCs are present in various tissues, recent single-cell RNA-seq studies have revealed the inter-tissue heterogeneity of MSCs. However, the functional significance of MSC heterogeneity and its role in aging remain unclear. Here, we investigated the properties of MSCs and their age-related changes in seven mouse tissues through histological, cell culture, and genetic examinations. The tissue of origin had a greater impact on the MSC transcriptome than aging. By first analyzing age-related changes, we found that Kera is exclusively expressed in muscle MSCs and significantly down-regulated by aging. Kera knockout mice recapitulated some sarcopenic phenotypes including reduced muscle mass and specific force, revealing the functional importance of Kera in the maintenance of muscle youth. These results suggest that MSCs have tissue-specific supportive functions and that deterioration in these functions may trigger tissue aging.
Keywords: heterogeneity; keratocan; mesenchymal stromal cells; platelet‐derived growth factor receptor‐alpha; sarcopenia.
© 2024 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Buechler, M. B. , Pradhan, R. N. , Krishnamurty, A. T. , Cox, C. , Calviello, A. K. , Wang, A. W. , Yang, Y. A. , Tam, L. , Caothien, R. , Roose‐Girma, M. , Modrusan, Z. , Arron, J. R. , Bourgon, R. , Müller, S. , & Turley, S. J. (2021). Cross‐tissue organization of the fibroblast lineage. Nature, 593(7860), 575–579. 10.1038/s41586-021-03549-5 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- JPMJPR2283/Japan Science and Technology Agency, PRESTO
- 18J21327/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
- 19H03125/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
- 19K22360/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
- 22J01118/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

