Exploring molecular targets in cancer: Unveiling the anticancer potential of Paeoniflorin through a comprehensive analysis of diverse signaling pathways and recent advances
- PMID: 39323487
- PMCID: PMC11423941
- DOI: 10.14440/jbm.2024.0003
Exploring molecular targets in cancer: Unveiling the anticancer potential of Paeoniflorin through a comprehensive analysis of diverse signaling pathways and recent advances
Abstract
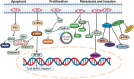
Tumors have posed significant threats to human health for over 250 years, emerging as the foremost cause of death. While chemotherapeutic drugs are effective in treating tumors, their side effects can sometimes be challenging to manage during therapy. Nonetheless, there is growing interest in exploring natural compounds as alternatives, which potentially achieve therapeutic outcomes comparable to conventional chemotherapeutics with fewer adverse effects. Paeoniflorin (PF), a monoterpene glycoside derived from the root of Paeonia lactiflora, has garnered significant attention lately due to its promising anti-cancer properties. This review offers an updated outline of the molecular mechanisms underlying PF's anti-tumor function, with a focus on its modulation of various signaling pathways. PF exerts its anti-tumor activity by regulating crucial cellular processes including apoptosis, angiogenesis, proliferation, and metastasis. We explored the multifaceted impact of PF while modulating through signaling pathways, encompassing nuclear factor kappa B, NOTCH, caspase cascade, transforming growth factor-β, NEDD4, P53/14-3-3, STAT 3, MAPK, MMP-9, and SKP2 signaling pathways, highlighting its versatility in targeting diverse malignancies. Furthermore, we discuss future research directions aimed at exploring innovative and targeted cancer therapies facilitated by PF.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer; Natural compound; Paeoniflorin; Signaling pathway.
© 2024 The Journal of Biological Methods, All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The multifaceted mechanisms of Paeoniflorin in the treatment of tumors: State-of-the-Art.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 May;149:112800. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112800. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35279012 Review.
-
Contents of paeoniflorin and albiflorin in two Korean landraces of Paeonia lactiflora and characterization of paeoniflorin biosynthesis genes in peony.Genes Genomics. 2024 Sep;46(9):1107-1122. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01553-3. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39126602
-
Analgesic effect of paeoniflorin in rats with neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral hyperalgesia is mediated through adenosine A(1) receptor by inhibiting the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) pathway.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009 Nov;94(1):88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.07.013. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009. PMID: 19664651
-
Paeoniflorin prevents hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Apr 27;9:2511-8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S102422. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27175085 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the action of carcinogens in gastric cancer with a glimpse into targeted therapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Dec;45(6):1073-1117. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00715-3. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36149600 Review.
References
-
- GlobalSurg Collaborative and National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit on Global Surgery. Global variation in postoperative mortality and complications after cancer surgery:A multicentre, prospective cohort study in 82 countries. Lancet. 2021;397(10272):387-397. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00001-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous