Evaluation of Dentofacial Angles in Children with Severe Adenoid Hypertrophy
- PMID: 39323500
- PMCID: PMC11421768
- DOI: 10.22038/ijorl.2024.77257.3584
Evaluation of Dentofacial Angles in Children with Severe Adenoid Hypertrophy
Abstract
Introduction: Hypertrophy of adenoids is a common condition in childhood, resulting in obstructive symptoms such as sleep apnea, snoring, and rhinosinusitis. Adenotonsillectomy is recommended to improve prognosis and quality of life. This case-control study compared facial angles and lip position related to dentofacial and mouth growth in symptomatic children with adenoid hypertrophy and asymptomatic control groups.
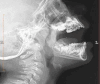
Materials and methods: The study included children aged 5 to 7 who presented with obstructive symptoms and confirmed severe adenoid hypertrophy in lateral neck radiography. Standard lateral photography was taken. The Nasofacial and Nasomental angles, and upper and lower lip positions and their distance behind the Ricketts line, were measured and compared with the normal control group.
Results: This study included 54 children with severe adenoid hypertrophy and 66 normal children. Facial angles were not significantly different between the two groups, but the mean horizontal position of the upper and lower lip in children with adenoid hypertrophy was significantly lower than in the control group (P value = 0.05). The lips were too close to the Ricketts line compared with the control group.
Conclusions: This research demonstrates that children with severe adenoid hypertrophy have more dentofacial disorders than others. Adenotonsillectomy surgery is necessary for children with obstructive symptoms caused by tonsil enlargement, and if symptoms like snoring persist post-surgery, complementary orthodontic treatments should be considered.
Keywords: Adenoid Hypertrophy; Adenotonsillectomy; Facial angle; Facial deformity; Sleep Apnea; Snoring.
© 2024 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of neck radiography in assessing recurrent/residual adenoid hypertrophy in children with OSA and history of adenotonsillectomy: a sleep physician perspective.J Clin Sleep Med. 2023 Jun 1;19(6):1027-1033. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.10468. J Clin Sleep Med. 2023. PMID: 36727478 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of rapid palatal expansion on the size of adenoids and tonsils in children.Sleep Med. 2022 Apr;92:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 35390750 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Impact of Preoperative Tonsil and Adenoid Size on Symptomatic Outcomes Following Adenotonsillectomy in Pediatric Patients.Cureus. 2023 Oct 16;15(10):e47093. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47093. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021551 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of adenotonsillectomy on the dentofacial development of obstructed children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2017 Oct 1;39(5):509-518. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjx005. Eur J Orthod. 2017. PMID: 28379334
-
Adenoidectomy: current approaches and review of the literature.Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2016 May-Jun;26(3):181-90. doi: 10.5606/kbbihtisas.2016.32815. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2016. PMID: 27107607 Review.
References
-
- Aydin S, Sanli A, Celebi O, Taşdemir Ö, Paksoy M, Eken M, et al. Prevalence of adenoid hypertrophy and nocturnal enuresis in primary school children in Istanbul, Turkey. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 May;72(5):665. - PubMed
-
- Kara CO, Ergin H, Koçak G, Kiliç İ, Yurdakul M. Prevalence of tonsillar hypertrophy and associated oropharyngeal symptoms in primary school children in Denizli, Turkey. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2002Nov. 66(2):175–179. - PubMed
-
- Tuncer Ü, Aydogan B, Soylu L, Simsek M, Akcali C, Kucukcan A. Chronic rhinosinusitis and adenoid hypertrophy in children. Am J Otolaryngol. 2004 Jan;25(1):5–10. - PubMed
-
- Havas T, Lowinger D. Obstructive adenoid tissue: an indication for powered-shaver adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg . 2002 Jul;128(7):789–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
