DJ-1 regulates mitochondrial function and promotes retinal ganglion cell survival under high glucose-induced oxidative stress
- PMID: 39323632
- PMCID: PMC11422208
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1455439
DJ-1 regulates mitochondrial function and promotes retinal ganglion cell survival under high glucose-induced oxidative stress
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the antioxidative and neuroprotective effects of DJ-1 in mitigating retinal ganglion cell (RGC) damage induced by high glucose (HG).
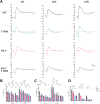
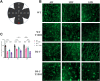
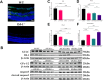
Methods: A diabetic mouse model and an HG-induced R28 cell model were employed for loss- and gain-of-function experiments. The expression levels of apoptosis and oxidative stress-related factors, including Bax, Bcl-2, caspase3, Catalase, MnSOD, GCLC, Cyto c, and GPx-1/2, were assessed in both animal and cell models using Western blotting. Retinal structure and function were evaluated through HE staining, electroretinogram, and RGC counting. Mitochondrial function and apoptosis were determined using JC-1 and TUNEL staining, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) measurement.
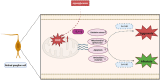
Results: In the mouse model, hyperglycemia resulted in reduced retinal DJ-1 expression, retinal structural and functional damage, disrupted redox protein profiles, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Elevated glucose levels induced mitochondrial impairment, ROS generation, abnormal protein expression, and apoptosis in R28 cells. Augmenting DJ-1 expression demonstrated a restoration of mitochondrial homeostasis and alleviated diabetes-induced morphological and functional impairments both in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusion: This study provides novel insights into the regulatory role of DJ-1 in mitochondrial dynamics, suggesting a potential avenue for enhancing RGC survival in diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: DJ-1; diabetic retinopathy; mitochondria; oxidative stress; retinal ganglion cells.
Copyright © 2024 Peng, Li, Ma, Sun and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
DJ-1/PARK7 inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress to prevent retinal pericyte apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Dec;189:107830. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107830. Epub 2019 Oct 5. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31593688
-
DJ-1 protects retinal pericytes against high glucose-induced oxidative stress through the Nrf2 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 12;10(1):2477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59408-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32051471 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of He-Ying-Qing-Re formula on retinal ganglion cell in diabetic retinopathy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 25;214:179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.018. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29253613
-
Protective Effects of Hesperidin (Citrus Flavonone) on High Glucose Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in a Cellular Model for Diabetic Retinopathy.Nutrients. 2017 Dec 2;9(12):1312. doi: 10.3390/nu9121312. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29207476 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Therapeutic Potential of Phosphocreatine in Diabetic Retinopathy: Mitigating Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis via JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jan 17;74(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s12031-023-02175-2. J Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38231435
Cited by
-
DJ-1 Promotes Diabetic Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing by Attenuating Hyperglycemia-Induced Oxidative Stress Through Inhibiting PTEN.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jul 1;66(9):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.9.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40626806 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese Superoxide Dismutase: Structure, Function, and Implications in Human Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;14(7):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DJ-1 Serves as a Central Regulator of Diabetes Complications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Aug 4;47(8):613. doi: 10.3390/cimb47080613. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40864767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial quality control in diabetes mellitus and complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Aug 27;16(1):652. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07936-y. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40866350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics in exploring the pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Dec 11;12:1500474. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1500474. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39723239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amato R., Catalani E., Dal Monte M., Cammalleri M., Cervia D., Casini G. (2022). Morpho-functional analysis of the early changes induced in retinal ganglion cells by the onset of diabetic retinopathy: the effects of a neuroprotective strategy. Pharmacol. Res. 185, 106516. 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106516 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

