Protective effect of salvianolic acid B against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: preclinical systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39323645
- PMCID: PMC11422085
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1452545
Protective effect of salvianolic acid B against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: preclinical systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Salvianolic acid B is the most abundant water-soluble component in the traditional Chinese medicine Danshen and can reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (MI/R) injury through multiple targets and pathways. However, the role of SalB in protecting the myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injury remains unclear.
Purpose: To perform a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the efficacy of Sal B in an animal model of myocardial infarction/reperfusion (MI/R) and to summarize the potential mechanisms of Sal B against MI/R.
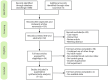
Methods: Studies published from inception to March 2024 were systematically searched in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Wanfang, and VIP databases. The methodological quality was determined using the SYRCLE RoB tool. The R software was used to analyze the data. The potential mechanisms are categorized and summarized.
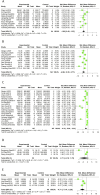
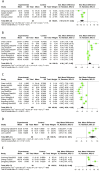
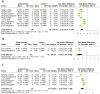
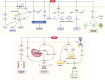
Results: 32 studies containing 732 animals were included. The results of the meta-analysis showed that Sal B reduced myocardial infarct size (p < 0.01), and the cardiological indices of CK-MB (p < 0.01), CK (p < 0.01), LDH (p < 0.01), and cTnI (p < 0.01) compared to the control group. In addition, Sal B increased cardiac function indices, such as LVFS (p < 0.01), -dp/dt max (p < 0.01), +dp/dt max (p < 0.01), and cardiac output (p < 0.01). The protective effects of Sal B on the myocardium after I/R may be mediated by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation, promoting neovascularization, regulating vascular function, and attenuating cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Publication bias was observed in all the included studies. Further studies are required to elucidate the extent of the cardioprotective effects of SalB and the safety of its use.
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis of Sal B in the treatment of MI/R injury, and Sal B demonstrated a positive effect on MI/R injury through the modulation of key pathological indicators and multiple signaling pathways. Further studies are needed to elucidate the extent to which SalB exerts its cardioprotective effects and the safety of its use.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/.
Keywords: animal model; metaanalysis; myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion; preclinical studies; salvianolic acid B(Sal B).
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Sun, Sun, Zhang, Tong, Zhang and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cardioprotective effect of curcumin on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: a meta-analysis of preclinical animal studies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 22;14:1184292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1184292. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37284318 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence construction of baicalin for treating myocardial ischemia diseases: A preclinical meta-analysis.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154476. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154476. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36191551
-
Hydroxysafflor yellow A for ischemic heart diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal experiments.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1510657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1510657. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40271057 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the interventional effects of resveratrol in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 19;15:1301502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1301502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38313308 Free PMC article.
-
SALVIANOLIC ACID B ALLEVIATING MYOCARDIUM INJURY IN ISCHEMIA REPERFUSION RATS.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 3;13(4):157-161. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i4.20. eCollection 2016. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 28852731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen H. X., Xu L., Xu B. H. (2012). Effect of salvianolic acid B on angiogenesis of ischemic myocardium in myocardial ischemia rats. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional. 18, 180–183. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2012.20.056 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

