Steroids in the Management of Ionotropic-Resistant Septic Shock: A Comprehensive Review of Efficacy and Outcomes
- PMID: 39323670
- PMCID: PMC11423274
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67795
Steroids in the Management of Ionotropic-Resistant Septic Shock: A Comprehensive Review of Efficacy and Outcomes
Abstract
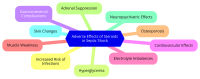
Septic shock is a critical condition characterized by persistent hypotension despite adequate fluid resuscitation and the use of vasopressors, often accompanied by multi-organ dysfunction. A challenging subset, ionotropic-resistant septic shock, persists despite ionotropic support. Steroids have been explored as a treatment for septic shock due to their anti-inflammatory properties and potential to improve hemodynamic stability. This review aims to evaluate the efficacy and outcomes of steroid therapy in managing ionotropic-resistant septic shock, assessing its impact on mortality, hemodynamic parameters, and adverse effects. A comprehensive review of the current literature, including randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and clinical guidelines, was conducted. Key studies, such as the CORTICUS and ADRENAL trials, were analyzed to determine the effectiveness of steroid regimens, specifically low-dose hydrocortisone, in patients with septic shock resistant to ionotropic agents. Evidence from recent trials indicates that low-dose hydrocortisone therapy can improve hemodynamic stability and reduce mortality in patients with septic shock, including those with ionotropic resistance. However, the benefits may vary depending on the timing of intervention, patient characteristics, and the presence of contraindications. Steroid therapy is associated with potential adverse effects, including secondary infections, glucose dysregulation, and gastrointestinal issues. Steroid therapy, particularly low-dose hydrocortisone, appears to be an effective adjunctive treatment for ionotropic-resistant septic shock, offering improved shock reversal and reduced mortality. Nonetheless, careful consideration of the risks and benefits is essential, and ongoing research is needed to refine treatment protocols and optimize patient outcomes. This review provides a detailed synthesis of current evidence and offers recommendations for clinical practice and future research in the management of septic shock resistant to ionotropic agents.
Keywords: hemodynamic stability; hydrocortisone; ionotropic resistance; mortality reduction; septic shock; steroid therapy.
Copyright © 2024, Nagaraju et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A double-edged sword: a narrative review on steroids in sepsis and septic shock.Intern Emerg Med. 2025 Jun 11. doi: 10.1007/s11739-025-04008-z. Online ahead of print. Intern Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40500516 Review.
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
-
Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012.Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580-637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23353941
-
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012.Intensive Care Med. 2013 Feb;39(2):165-228. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Intensive Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23361625 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose corticosteroids in septic shock: Has the pendulum shifted?Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019 Apr 8;76(8):493-500. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxz017. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30851043 Review.
References
-
- Septic shock: practice essentials, background, pathophysiology. August. [ Apr; 2024 ]. 2023. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/168402-overview https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/168402-overview
-
- Chakraborty RK, Burns B. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome. - PubMed
-
- Morelli A, Passariello M, Singer M. Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2014. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2014. Inotropic support in the treatment of septic myocardial dysfunction: pathophysiological implications supporting the use of levosimendan; pp. 407–419.
-
- Corticosteroids for septic shock. Annane D. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:0–20. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources