Bone-targeting engineered milk-derived extracellular vesicles for MRI-assisted therapy of osteoporosis
- PMID: 39323741
- PMCID: PMC11422186
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae112
Bone-targeting engineered milk-derived extracellular vesicles for MRI-assisted therapy of osteoporosis
Abstract
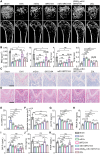
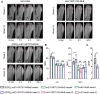
The imbalance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts is the cause of osteoporosis. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles (mEVs), excellent drug delivery nanocarriers, can promote bone formation and inhibit bone resorption. In this study, we conjugated bone-targeting peptide (AspSerSer, DSS)6 to mEVs by click chemistry and then loaded with SRT2104, a SIRT1 (silent mating-type information regulation 2 homolog 1) agonist that was proofed to help reduce bone loss. The engineered (DSS)6-mEV-SRT2104 had the intrinsic anti-osteoporosis function of mEVs and SRT2104 to reverse the imbalance in bone homeostasis by simultaneously regulating osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. Furthermore, we labelled mEVs with MnB nanoparticles that can be used for the in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) visualization. The obtained nanocomposites significantly prevented bone loss in osteoporosis mice and increased bone mineral density, exhibiting superior bone accumulation under MRI. We believe the proposed (DSS)6-mEV-SRT2104/MnB provides a novel paradigm for osteoporosis treatment and monitoring.
Keywords: MRI; SRT2104; bone-targeting peptide; milk-derived extracellular vesicles; osteoporosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
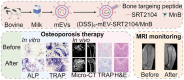


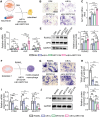
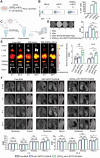
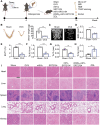
Similar articles
-
Oral Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Osteoclastogenesis and Ameliorate Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice by Improving Gut Microbiota.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Mar 6;72(9):4726-4736. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07095. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38294408
-
Bone-Targeting Peptide and RNF146 Modified Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Osteoporosis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 17;19:471-488. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S433511. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38250192 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Bovine Milk Extracellular Vesicles on Alveolar Bone Loss.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Feb;68(3):e2300445. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202300445. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024. PMID: 38087782
-
Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Perspective on Comparative Therapeutics and Targeted Nanocarrier Application.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Nov 15;12(11):1282. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12111282. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating osteoclasts with nanoparticles: A path for osteoporosis management?Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023 Jul-Aug;15(4):e1885. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1885. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37037204 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted delivery of extracellular vesicles: the mechanisms, techniques and therapeutic applications.Mol Biomed. 2024 Nov 21;5(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00230-x. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39567444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as vital players in drug delivery: a focus on clinical disease treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 May 14;13:1600227. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1600227. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40438295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin-primed milk-derived extracellular vesicles remodel hair follicle microenvironment for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia.Regen Biomater. 2025 May 30;12:rbaf051. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbaf051. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40735523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kemp JP, Morris JA, Medina-Gomez C, Forgetta V, Warrington NM, Youlten SE, Zheng J, Gregson CL, Grundberg E, Trajanoska K, Logan JG, Pollard AS, Sparkes PC, Ghirardello EJ, Allen R, Leitch VD, Butterfield NC, Komla-Ebri D, Adoum AT, Curry KF, White JK, Kussy F, Greenlaw KM, Xu C, Harvey NC, Cooper C, Adams DJ, Greenwood CMT, Maurano MT, Kaptoge S, Rivadeneira F, Tobias JH, Croucher PI, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Bassett JHD, Williams GR, Richards JB, Evans DM.. Identification of 153 new loci associated with heel bone mineral density and functional involvement of GPC6 in osteoporosis. Nat Genet 2017;49:1468–75. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naot D, Musson DS, Cornish J.. The activity of peptides of the calcitonin family in bone. Physiol Rev 2019;99:781–805. - PubMed
-
- Händel MN, Cardoso I, von Bülow C, Rohde JF, Ussing A, Nielsen SM, Christensen R, Body JJ, Brandi ML, Diez-Perez A, Hadji P, Javaid MK, Lems WF, Nogues X, Roux C, Minisola S, Kurth A, Thomas T, Prieto-Alhambra D, Ferrari SL, Langdahl B, Abrahamsen B.. Fracture risk reduction and safety by osteoporosis treatment compared with placebo or active comparator in postmenopausal women: systematic review, network meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 2023;381:e068033. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

