Integrating machine learning for the optimization of polyacrylamide/alginate hydrogel
- PMID: 39323746
- PMCID: PMC11422183
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae109
Integrating machine learning for the optimization of polyacrylamide/alginate hydrogel
Abstract
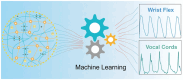
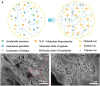
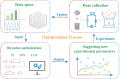
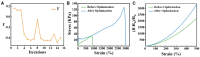
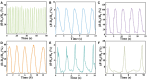
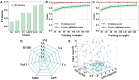
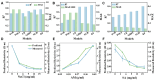
Hydrogels are highly promising due to their soft texture and excellent biocompatibility. However, the designation and optimization of hydrogels involve numerous experimental parameters, posing challenges in achieving rapid optimization through conventional experimental methods. In this study, we leverage machine learning algorithms to optimize a dual-network hydrogel based on a blend of acrylamide (AM) and alginate, targeting applications in flexible electronics. By treating the concentrations of components as experimental parameters and utilizing five material properties as evaluation criteria, we conduct a comprehensive property assessment of the material using a linear weighting method. Subsequently, we design a series of experimental plans using the Bayesian optimization algorithm and validate them experimentally. Through iterative refinement, we optimize the experimental parameters, resulting in a hydrogel with superior overall properties, including heightened strain sensitivity and flexibility. Leveraging the available experimental data, we employ a classification algorithm to separate the cutoff data. The feature importance identified by the classification model highlights the pronounced impact of AM, ammonium persulfate, and N,N-methylene on the classification outcomes. Additionally, we develop a regression model and demonstrate its utility in predicting and analyzing the relationship between experimental parameters and hydrogel properties through experimental validation.
Keywords: Bayesian optimization; alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel; flexible electronics; machine learning; stretchability.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tannic Acid-Silver Dual Catalysis Induced Rapid Polymerization of Conductive Hydrogel Sensors with Excellent Stretchability, Self-Adhesion, and Strain-Sensitivity Properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Dec 16;12(50):56509-56521. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c18250. Epub 2020 Dec 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 33270440
-
Integrating DFT and machine learning for the design and optimization of sodium alginate-based hydrogel adsorbents: Efficient removal of pollutants from wastewater.Environ Res. 2024 Apr 15;247:118219. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118219. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38253197
-
Ultrastretchable, Antifreezing, and High-Performance Strain Sensor Based on a Muscle-Inspired Anisotropic Conductive Hydrogel for Human Motion Monitoring and Wireless Transmission.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Sep 28;14(38):43833-43843. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c14120. Epub 2022 Sep 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36112731
-
Recent advances in flexible hydrogel sensors: Enhancing data processing and machine learning for intelligent perception.Biosens Bioelectron. 2024 Oct 1;261:116499. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116499. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024. PMID: 38896981 Review.
-
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Electronics.Adv Mater. 2023 Apr;35(14):e2205326. doi: 10.1002/adma.202205326. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 36037508 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-Generation Hydrogel Design: Computational Advances in Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 16;17(10):1373. doi: 10.3390/polym17101373. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li P, Sun W, Li J, Chen J-P, Wang X, Mei Z, Jin G, Lei Y, Xin R, Yang M, Xu J, Pan X, Song C, Deng X-Y, Lei X, Liu K, Wang X, Zheng Y, Zhu J, Lv S, Zhang Z, Dai X, Lei T.. N-type semiconducting hydrogel. Science 2024;384:557–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

