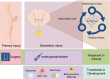
Prussian blue nanotechnology in the treatment of spinal cord injury: application and challenges
- PMID: 39323764
- PMCID: PMC11422158
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1474711
Prussian blue nanotechnology in the treatment of spinal cord injury: application and challenges
Abstract
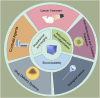
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a serious neurological condition that currently lacks effective treatments, placing a heavy burden on both patients and society. Prussian blue nanoparticles exhibit great potential for treating spinal cord injuries due to their excellent physicochemical properties and biocompatibility. These nanoparticles have strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capabilities, effectively scavenge free radicals, and reduce oxidative stress damage to cells. Prussian blue nanotechnology shows broad application potential in drug delivery, bioimaging, cancer therapy, anti-inflammatory and oxidative stress treatment, and biosensors. This article reviewed the potential applications of Prussian blue nanotechnology in treating spinal cord injuries, explored the challenges and solutions associated with its application, and discussed the future prospects of this technology in SCI treatment.
Keywords: Prussian blue nanotechnology; inflammation; oxidative stress; spinal cord injury; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Gu, Zhang and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prussian blue analogues improves the microenvironment after spinal cord injury by regulating Zn.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111868. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111868. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38493692
-
High rapamycin-loaded hollow mesoporous Prussian blue nanozyme targets lesion area of spinal cord injury to recover locomotor function.Biomaterials. 2023 Dec;303:122358. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122358. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Biomaterials. 2023. PMID: 37951099
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits neuro-inflammation and oxidative stress following spinal cord injury by mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction via the SIRT1/PGC1α/DRP1 signaling pathway.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 25;22(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05089-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38528569 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements of Prussian blue-based nanoplatforms in biomedical fields: Progress and perspectives.J Control Release. 2022 Nov;351:752-778. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.007. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36216173 Review.
-
Nanotechnology for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021 Aug;27(4):353-365. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0188. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021. PMID: 33135599 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial Transplantation/Transfer: Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Spinal Cord Injury.J Orthop Translat. 2025 May 16;52:441-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.04.017. eCollection 2025 May. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40485848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources