MLAFP-XN: Leveraging neural network model for development of antifungal peptide identification tool
- PMID: 39323787
- PMCID: PMC11422610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37820
MLAFP-XN: Leveraging neural network model for development of antifungal peptide identification tool
Abstract
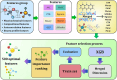
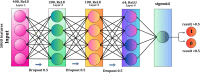
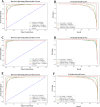
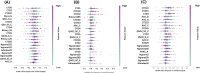
Infectious fungi have been an increasing global concern in the present era. A promising approach to tackle this pressing concern involves utilizing Antifungal peptides (AFP) to develop an antifungal drug that can selectively eliminate fungal pathogens from a host with minimal toxicity to the host. Accordingly, identifying precise therapeutic antifungal peptides is crucial for developing effective drugs and treatments. This study proposed MLAFP-XN, a neural network-based strategy for accurately detecting active AFP in sequencing data to achieve this objective. In this work, eight feature extraction techniques and the XGB feature selection strategy are utilized together to present an enhanced methodology. A total of 24 classification models were evaluated, and the most effective four have been selected. Each of these models demonstrated superior accuracy on independent test sets, with respective scores of 97.93 %, 99.47 %, and 99.48 %. Our model outperforms current state of the art methods. In addition, we created a companion website to demonstrate our AFP recognition process and use SHAP to identify the most influential properties.
Keywords: Antifungal drug; Antifungal peptide; Drug discovery; Feature extraction; Feature selection; Neural network.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AFP-MFL: accurate identification of antifungal peptides using multi-view feature learning.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jan 19;24(1):bbac606. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac606. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36631407
-
DeepAFP: An effective computational framework for identifying antifungal peptides based on deep learning.Protein Sci. 2023 Oct;32(10):e4758. doi: 10.1002/pro.4758. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37595093 Free PMC article.
-
A self-assembling peptide inhibits the growth and function of fungi via a wrapping strategy.Biomater Sci. 2024 Feb 13;12(4):990-1003. doi: 10.1039/d3bm01845h. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 38193333
-
Fungal Infections as an Uprising Threat to Human Health: Chemosensitization of Fungal Pathogens With AFP From Aspergillus giganteus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 May 25;12:887971. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.887971. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35694549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic Peptides with Antifungal Properties Derived from Bacteria, Fungi, Plants, and Synthetic Sources.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 18;16(6):892. doi: 10.3390/ph16060892. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AAindexNC: Estimating the Physicochemical Properties of Non-Canonical Amino Acids, Including Those Derived from the PDB and PDBeChem Databank.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 22;25(23):12555. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312555. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684267 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

