Intermittent hypoxic training - derived exosomes in stroke rehabilitation
- PMID: 39323911
- PMCID: PMC11422222
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2024.1475234
Intermittent hypoxic training - derived exosomes in stroke rehabilitation
Abstract
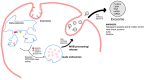
Ischemic stroke is the fourth leading cause of adult disability in the US, and it is a huge social burden all over the world. However, the efficient treatment of ischemic stroke is not available. An apparent reason for failing to find or develop an intervention for ischemic stroke is contributed to the tight blood-brain barrier (BBB). The unique characteristics of exosomes that can traverse BBB have been highlighted among researchers investigating interventions for ischemic stroke conditions. Additionally, intermittent hypoxic training has been considered a potential intervention in the treatment or rehabilitation process of ischemic stroke patients. In this mini-review, we are going to review the possibility of applying exosomes produced by a subject who does intermittent hypoxic conditioning in a treatment program for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Neuroprotection; exosome; hypoxia; intermittent hypoxic training (IHT); microglia; stroke.
Copyright © 2024 Ryou and Burton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Normobaric intermittent hypoxic training regulates microglia phenotype and enhances phagocytic activity.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Apr;245(8):740-747. doi: 10.1177/1535370220919361. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32299228 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of Exosomes in Ischemic Stroke Treatment.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 11;12(1):115. doi: 10.3390/biom12010115. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35053263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Jan 19;769:136389. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136389. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 34896256
-
Exosomes in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy of ischemic stroke.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 16;10:980548. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.980548. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36588958 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia training protects cerebrovascular function in Alzheimer's disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Jun;241(12):1351-63. doi: 10.1177/1535370216649060. Epub 2016 May 10. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27190276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ClinicalTrials.gov . (2016). A study evaluating the safety and efficacy of PF-03049423 in subjects with ischemic stroke. Available at: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01208233
-
- Cui G. H., Wu J., Mou F. F., Xie W. H., Wang F. B., Wang Q. L., et al. . (2018). Exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate cognitive decline by rescuing synaptic dysfunction and regulating inflammatory responses in APP/PS1 mice. FASEB J. 32, 654–668. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700600R, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Di Cesare F., Mancuso J., Woodward P., Bednar M. M., Loudon P. T., A9541004 Stroke Study Group (2016). Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor PF-03049423 effect on stroke recovery: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 25, 642–649. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.11.026, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources