New insights in lipid metabolism: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39323915
- PMCID: PMC11422391
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1430465
New insights in lipid metabolism: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
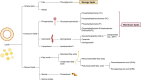
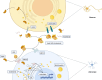
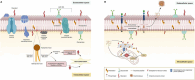
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is increasingly recognized as being intertwined with the dysregulation of lipid metabolism. Lipids are a significant class of nutrients vital to all organisms, playing crucial roles in cellular structure, energy storage, and signaling. Alterations in the levels of various lipids in AD brains and dysregulation of lipid pathways and transportation have been implicated in AD pathogenesis. Clinically, evidence for a high-fat diet firmly links disrupted lipid metabolism to the pathogenesis and progression of AD, although contradictory findings warrant further exploration. In view of the significance of various lipids in brain physiology, the discovery of complex and diverse mechanisms that connect lipid metabolism with AD-related pathophysiology will bring new hope for patients with AD, underscoring the importance of lipid metabolism in AD pathophysiology, and promising targets for therapeutic intervention. Specifically, cholesterol, sphingolipids, and fatty acids have been shown to influence amyloid-beta (Aβ) accumulation and tau hyperphosphorylation, which are hallmarks of AD pathology. Recent studies have highlighted the potential therapeutic targets within lipid metabolism, such as enhancing apolipoprotein E lipidation, activating liver X receptors and retinoid X receptors, and modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Ongoing clinical trials are investigating the efficacy of these strategies, including the use of ketogenic diets, statin therapy, and novel compounds like NE3107. The implications of these findings suggest that targeting lipid metabolism could offer new avenues for the treatment and management of AD. By concentrating on alterations in lipid metabolism within the central nervous system and their contribution to AD development, this review aims to shed light on novel research directions and treatment approaches for combating AD, offering hope for the development of more effective management strategies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; diet; lipid; lipid metabolism; therapy strategies.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Zhao, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of cholesterol metabolism with Phytoremedies in Alzheimer's disease: A comprehensive review.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Aug;99:102389. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102389. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38906182 Review.
-
microRNA-33 Regulates ApoE Lipidation and Amyloid-β Metabolism in the Brain.J Neurosci. 2015 Nov 4;35(44):14717-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2053-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26538644 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lipids and Membranes in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive View.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018;15(13):1191-1212. doi: 10.2174/1567205015666180911151716. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018. PMID: 30207230 Review.
-
Decoding Alzheimer's disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: implications for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Sep;108:21-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23850509 Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Fingolimod in Alzheimer's Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Neuromolecular Med. 2019 Sep;21(3):227-238. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08558-2. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Neuromolecular Med. 2019. PMID: 31313064 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocytic Pathways Unveil the Role of Syndecans in the Seeding and Spreading of Pathological Protein Aggregates: Insights into Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 24;26(9):4037. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094037. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Predictors of Cognitive Impairment in a Cohort of Patients with Older Age Bipolar Disorder.Brain Sci. 2025 Mar 27;15(4):349. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15040349. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40309802 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Regulators of Amyloidogenic Pathway of APP Processing in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 20;13(7):1513. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071513. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathology and Treatments of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Considering Changes in Brain Energy Metabolism Due to Type 2 Diabetes.Molecules. 2024 Dec 16;29(24):5936. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245936. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy Metabolism and Brain Aging: Strategies to Delay Neuronal Degeneration.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 21;45(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01555-z. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40259102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

