Evaluating the feasibility and utility of telephonic motivational interviewing in older adults
- PMID: 39323932
- PMCID: PMC11422548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pecinn.2024.100344
Evaluating the feasibility and utility of telephonic motivational interviewing in older adults
Abstract
Older adults face unique barriers and challenges related to physical activity (PA) participation. Motivational interviewing (MI) is a commonly used health coaching strategy to support behavior change that holds potential for older adults. Previous research on MI strategies has focused primarily on face-to-face delivery, limiting insights regarding virtual programs.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine if MI could be delivered telephonically with high fidelity and high acceptability in older adult participants. The study is designed to inform future trials evaluating its effectiveness in supporting virtual PA programs.
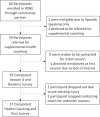
Methods: This study evaluated the feasibility and acceptability of telephonic MI among older adults that enrolled in an online version of the Walk with Ease program.
Results: Of 39 participants referred, 29 enrolled and 27 provided feedback. Participants were highly accepting and adherent, with 74 % of patients attending at least five of six sessions, and 96 % of participants indicating satisfaction with the MI provided. Coaches improved program enjoyment by helping set effective goals and providing ongoing accountability.
Conclusions: Evaluations documented adequate fidelity and high acceptability of telephonic delivery, and motivation results revealed large, significant increases in autonomous regulation (quality of motivation).
Innovation: Telephonic MI using non-healthcare professional coaches is feasibly delivered with high fidelity, and is acceptable to older adult participants. The innovative delivery format offers novel opportunities supporting virtual and telehealth interventions to reduce chronic disease risk among older adults.
Keywords: Intervention acceptability; Motivational interviewing; Older adult; Physical activity; Telehealth.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on Glycemic Control for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DM2): A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-17. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-246. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820150
-
Virtual motivational interviewing for physical activity among older adults: A non-randomised, mixed-methods feasibility study.Int J Psychol. 2025 Feb;60(1):e13269. doi: 10.1002/ijop.13269. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Int J Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39552399 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Motivational Interviewing (VIMINT) to support physical activity: Experiences of older adults and counsellors.J Health Psychol. 2024 Oct;29(12):1416-1430. doi: 10.1177/13591053241235094. Epub 2024 Feb 27. J Health Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38414103 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for improving adherence to inhaled therapies in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 29;3(3):CD013766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013766.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36989170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motivational Interviewing as a Strategy to Impact Outcomes in Heart Failure Patients: A Systematic Review.Patient. 2020 Feb;13(1):43-55. doi: 10.1007/s40271-019-00387-6. Patient. 2020. PMID: 31502239
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of a Telephone-Delivered Walk With Ease Program on Arthritis-Related Symptoms, Function, and Activity: A Randomized Trial.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025 Jul;77(7):928-938. doi: 10.1002/acr.25515. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40026069 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bevington F., Piercy K.L., Olscamp K., Hilfiker S.W., Fisher D.G., Barnett E.Y. The move your way campaign: encouraging contemplators and families to meet the recommendations from the physical activity guidelines for Americans. J Phys Activity Health. 2020;17(4):397–403. - PubMed
-
- Schutzer K.A., Graves B.S. Barriers and motivations to exercise in older adults. Prev Med. 2004;39(5):1056–1061. - PubMed
-
- Spiteri K., Broom D., Bekhet A.H., De Caro J.X., Laventure B., Grafton K. Barriers and motivators of physical activity participation in middle-aged and older adults—a systematic review. J Aging Phys Act. 2019;27(6):929–944. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources