The potential of retinoic acid receptors as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer
- PMID: 39323992
- PMCID: PMC11422079
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1453934
The potential of retinoic acid receptors as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer is a heterogeneous collection of tumors characterized by low survival rates. All-trans retinoic acid (retinoic-acid) is a clinically useful therapeutic agent belonging to the chemical family of retinoids, which consists of both natural and synthetic derivatives of vitamin-A. Retinoids are essential components of the normal diet and they regulate different physiological processes. From a therapeutic point of view, retinoic-acid is the first example of clinically useful differentiating agent. Indeed, the differentiating properties of this compound have promoted the use of retinoic-acid as a standard of care in Acute-Promyelocytic-Leukemia, a rare form of acute myeloid leukemia. In this study, we determine the RNA expression of the six isoforms of Retinoic-Acid-Receptors (RARα/RARβ/RARγ/RXRα/RXRβ/RXRγ) in view of their potential use as gastric cancer progression markers and/or therapeutic targets. In addition, we evaluate associations between the expression of these receptors and a simplified molecular classification of stomach tumors as well as the clinical characteristics of the cohort of patients analyzed. Finally, we define the prognostic value of the various Retinoic-Acid-Receptors in gastric cancer.
Methods: In this single institution and retrospective RAR-GASTRIC study, we consider 55 consecutive gastric cancer patients. We extract total RNA from the pathological specimens and we perform a NanoString Assay using a customized panel of genes. This allows us to determine the expression levels of the RAR and RXR mRNAs as well as other transcripts of interest.
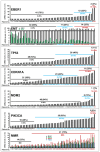
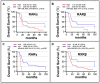
Results: Our data demonstrate ubiquitous expression of the RAR and RXR mRNAs in gastric cancers. High levels of RARα, RARβ, RXRα and RXRβ show a significant association with stage IV tumors, "de novo" metastatic disease, microsatellite-stable-status, epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition, as well as PIK3CA and TP53 expression. Finally, we observe a worse overall-survival in gastric cancer patients characterized by high RARα/RARβ/RARγ/RXRβ mRNA levels.
Conclusions: In gastric cancer, high expression levels of RARα/RARβ/RARγ/RXRβ transcripts are associated with poor clinical and molecular characteristics as well as with reduced overall-survival. Our data are consistent with the idea that RARα, RARβ, RARγ and RXRβ represent potential prognostic markers and therapeutic targets of gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric cancer; prognosticbiomarkers; retinoic-acid-receptors; retrospective-clinical-study; therapeutic-targets.
Copyright © 2024 Garattini, Basile, De Re, Brisotto, Miolo, Canzonieri, Aprile, Corvaja, Buriolla, Garattini and Puglisi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retinoid receptors in gastric cancer: expression and influence on prognosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(5):1809-17. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.5.1809. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012. PMID: 22901127
-
Sequence analysis of retinoic acid receptor alpha, beta and gamma isoforms in the lizard, Podarcis sicula.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 May;104(3-5):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.03.005. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17449240
-
Arginine of retinoic acid receptor beta which coordinates with the carboxyl group of retinoic acid functions independent of the amino acid residues responsible for retinoic acid receptor subtype ligand specificity.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003 Jan 15;409(2):375-84. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(02)00638-0. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003. PMID: 12504905
-
Molecular Interactions of Selective Agonists and Antagonists with the Retinoic Acid Receptor γ.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6568. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126568. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoids, rexinoids and their cognate nuclear receptors: character and their role in chemoprevention of selected malignant diseases.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2007 Dec;151(2):187-94. doi: 10.5507/bp.2007.033. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2007. PMID: 18345250 Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of H. pylori infection in HER2-positive gastric cancer cell lines: insights from Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1550651. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550651. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40642068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bang Y-J, Cutsem EV, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. . Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2010) 376:687–97. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61121-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, Garrido M, Salman P, Shen L, et al. . First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2021) 398:27–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00797-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

