Effects of occlusion pressure on hemodynamic responses recorded by near-infrared spectroscopy across two visits
- PMID: 39324105
- PMCID: PMC11422206
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1441239
Effects of occlusion pressure on hemodynamic responses recorded by near-infrared spectroscopy across two visits
Abstract
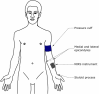
Ischemic Preconditioning (IPC) has emerged as a promising approach to mitigate the impact of hypoxia on physiological functions. However, the heterogeneity of occlusion pressures for inducing arterial occlusion has led to inconsistent hemodynamic outcomes across studies. This study aims to evaluate the peripheral hemodynamic responses to partial and total blood-flow occlusions on the left arm at rest, using absolute or individualized pressures, on two occasions. Thirty-five young males volunteered to participate in this study. IPC procedure (3 × 7-min) was performed on the left upper arm with cuff pressures at 50 mmHg (G1), 50 mmHg over the systolic blood pressure (SBP + 50 mmHg) (G2) or 250 mmHg (G3). NIRS-derived parameters were assessed for each occlusion and reperfusion phase in the brachioradialis. Results showed a significantly lower magnitude of deoxygenation (TSIAUC) for G1 compared to G2 (-1959.2 ± 1417.4 vs. -10908.1 ± 1607.5, P < 0.001) and G3 -1959.2 ± 1417.4 vs. -11079.3 ± 1828.1, P < 0.001), without differences between G2 and G3. However, G3 showed a significantly faster reoxygenation only for tissue saturation index (TSIslope) compared to G2 (1.3 ± 0.1 vs. 1.0 ± 0.2, P = 0.010), but without differences in the speed of recovery of deoxyhemoglobin [(HHb) slope], or in the magnitude of post-occlusive hyperemia (PORH). Besides TSI reoxygenation speed, G2 and G3 elicit comparable resting hemodynamic responses measured by NIRS. Thus, this study highlights the practicality and effectiveness of using relative occlusion pressures based on systolic blood pressure (SBP) rather than relying on excessively high absolute pressures.
Keywords: NIRS; arterial occlusion; blood flow restriction; muscle ischemia; muscle oxygenation; remote ischemic preconditioning.
Copyright © 2024 Desanlis, Gordon, French, Calveyrac, Cottin and Gernigon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Commentary: Effects of occlusion pressure on hemodynamic responses recorded by near-infrared spectroscopy across two visits.Front Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;15:1504497. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1504497. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39552723 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The influence of cuff location on the oxygenation and reperfusion of the foot during ischemic preconditioning: A reliability study.Microvasc Res. 2025 Jul;160:104811. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2025.104811. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Microvasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40246226 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra- and Inter-Day Reliability of the NIRS Portamon Device after Three Induced Muscle Ischemias.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 10;22(14):5165. doi: 10.3390/s22145165. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890846 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of muscle oxygenation response to vascular occlusion: implications for remote ischaemic preconditioning and physical Performance.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017 Nov;37(6):785-793. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12353. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017. PMID: 26934057 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of lower limb ischaemic preconditioning: a systematic review.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1323310. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1323310. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38274048 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Near Infrared Spectroscopy to Evaluate the Effect of Exercise on Peripheral Muscle Oxygenation in Patients with Lower Extremity Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 May;61(5):837-847. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.02.008. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33810977
Cited by
-
Commentary: Effects of occlusion pressure on hemodynamic responses recorded by near-infrared spectroscopy across two visits.Front Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;15:1504497. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1504497. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39552723 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bailey T. G., Birk G. K., Cable N. T., Atkinson G., Green D. J., Jones H., et al. (2012a). Remote ischemic preconditioning prevents reduction in brachial artery flow-mediated dilation after strenuous exercise. Am. J. Physiology. Heart Circulatory Physiology 303 (5), H533–H538. 10.1152/ajpheart.00272.2012 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

