The promise of Synovial Joint-on-a-Chip in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 39324139
- PMCID: PMC11422143
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1408501
The promise of Synovial Joint-on-a-Chip in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
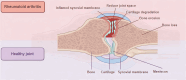
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affects millions of people worldwide, but there are limited drugs available to treat it, so acquiring a more comprehensive comprehension of the underlying reasons and mechanisms behind inflammation is crucial, as well as developing novel therapeutic approaches to manage it and mitigate or forestall associated harm. It is evident that current in vitro models cannot faithfully replicate all aspects of joint diseases, which makes them ineffective as tools for disease research and drug testing. Organ-on-a-chip (OoC) technology is an innovative platform that can mimic the microenvironment and physiological state of living tissues more realistically than traditional methods by simulating the spatial arrangement of cells and interorgan communication. This technology allows for the precise control of fluid flow, nutrient exchange, and the transmission of physicochemical signals, such as bioelectrical, mechanical stimulation and shear force. In addition, the integration of cutting-edge technologies like sensors, 3D printing, and artificial intelligence enhances the capabilities of these models. Here, we delve into OoC models with a particular focus on Synovial Joints-on-a-Chip, where we outline their structure and function, highlighting the potential of the model to advance our understanding of RA. We integrate the actual evidence regarding various OoC models and their possible integration for multisystem disease study in RA research for the first time and introduce the prospects and opportunities of the chip in RA etiology and pathological mechanism research, drug research, disease prevention and human precision medicine. Although many challenges remain, OoC holds great promise as an in vitro model that approaches physiology and dynamics.
Keywords: Organ-on-a-Chip; Synovial Joint-on-a-Chip; disease models; microphysiological systems; precision medicine; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Su, Wang, Wu, Fan, Bin, Gao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

