Radioactive Iodine-131 Therapy Reduced the Risk of MACEs and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly with Hyperthyroidism Combined with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 39324146
- PMCID: PMC11423839
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S484910
Radioactive Iodine-131 Therapy Reduced the Risk of MACEs and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly with Hyperthyroidism Combined with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to assess the efficacy of antithyroid drugs (ATDs) and radioactive iodine-131 (RAI) therapies in reducing the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and all-cause mortality in patients with hyperthyroidism complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: Between January 2013 and December 2021, 540 subjects were included in the analysis. All participants were followed up for 9 years, with a median of 54 months (2451 person-years). The subjects were categorized into two groups: the ATDs group (n = 414) and the RAI group (n = 126). According to the free triiodothyronine (FT3) tertiles, the patients receiving RAI were further grouped as follows: low-level (≤ 4.70 pmol/L, n = 42), moderate-level (4.70-12.98 pmol/L, n = 42), and high-level (≥ 12.98 pmol/L, n = 42). The efficacy of ATDs and RAI therapies in reducing the risk of MACEs and all-cause mortality was assessed.
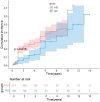
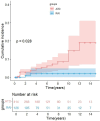
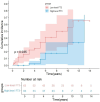
Results: Of the 540 participants, 163 experienced MACEs (30.19%), 25 (15.34%) of whom died. Multivariate Cox regression analyses revealed that RAI was associated with a 38.5% lower risk of MACEs (P = 0.016) and a 77.1% lower risk of all-cause mortality (P = 0.046). Stratified analyses indicated that RAI had a protective effect on MACEs in patients aged ≥ 60 years (P = 0.001, P for interaction = 0.031) and patients with a duration of diabetes mellitus ≥ 6 years (P = 0.013, P for interaction = 0.002). Kaplan‒Meier analysis revealed a lower cumulative incidence of MACEs and all-cause mortality in the RAI group (log-rank, all P < 0.05). Moreover, the ROC curve suggested an optimal FT3 cut-off value of 5.4 pmol/mL for MACE (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that RAI therapy effectively reduced the risk of MACEs and all-cause mortality in elderly patients with hyperthyroidism combined with T2DM.
Keywords: all-cause mortality; hyperthyroidism; major adverse cardiovascular events; radioactive iodine-131; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were reported by the authors in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of Risk Factors for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Stent Restenosis after Revascularization.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 May 18;24(5):146. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2405146. eCollection 2023 May. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076758 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Radioactive Iodine, Antithyroid Drug, and Surgical Treatments With Solid Cancer Mortality in Patients With Hyperthyroidism.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Jul 1;3(7):e209660. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.9660. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32701159 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Treatment Choices for Graves' Hyperthyroidism: A Historical Cohort Study.Thyroid. 2017 Apr;27(4):497-505. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0343. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Thyroid. 2017. PMID: 28049375 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Risk After Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Hyperthyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Sep 1;4(9):e2125072. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.25072. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34533571 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing the Efficacy of Radioactive Iodine Monotherapy versus Radioactive Iodine Therapy and Adjunctive Lithium for the Treatment of Hyperthyroidism.Endocr Res. 2021 Nov;46(4):160-169. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2021.1924769. Epub 2021 May 24. Endocr Res. 2021. PMID: 34028325
Cited by
-
Comparison of mortality and cardiovascular morbidity following treatment for hyperthyroidism: A systematic review and bayesian network meta-analysis.Endocrine. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04342-4. Online ahead of print. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 40629108
-
Process to radioactive iodine treatment for Graves' hyperthyroidism: condemned or absolved?J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Sep;48(9):1927-1950. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02653-x. Epub 2025 Aug 6. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40768183 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

