Expanding the field of view - a simple approach for interactive visualisation of electron microscopy data
- PMID: 39324375
- PMCID: PMC11529876
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.262198
Expanding the field of view - a simple approach for interactive visualisation of electron microscopy data
Abstract
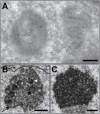
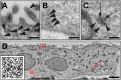
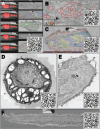
The unparalleled resolving power of electron microscopy is both a blessing and a curse. At 30,000× magnification, 1 µm corresponds to 3 cm in the image and the field of view is only a few micrometres or less, resulting in an inevitable reduction in the spatial data available in an image. Consequently, the gain in resolution is at the cost of loss of the contextual 'reference space', which is crucial for understanding the embedded structures of interest. This problem is particularly pronounced in immunoelectron microscopy, where the detection of a gold particle is crucial for the localisation of specific molecules. The common solution of presenting high-magnification and overview images side by side often insufficiently represents the cellular environment. To address these limitations, we propose here an interactive visualization strategy inspired by digital maps and GPS modules which enables seamless transitions between different magnifications by dynamically linking virtual low magnification overview images with primary high-resolution data. By enabling dynamic browsing, it offers the potential for a deeper understanding of cellular landscapes leading to more comprehensive analysis of the primary ultrastructural data.
Keywords: Data communication; Electron microscopy; Interactive visualization; Reference space; Teaching.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The author declares no competing or financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Virtual electron microscopy: a simple implementation creating a new paradigm in ultrastructural examination.Int J Surg Pathol. 2011 Oct;19(5):570-5. doi: 10.1177/1066896911421173. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Int J Surg Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21903681
-
Computer-assisted visualizations of neural networks: expanding the field of view using seamless confocal montaging.J Neurosci Methods. 2000 Jun 1;98(2):155-63. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00200-4. J Neurosci Methods. 2000. PMID: 10880829
-
Virtual electron microscopy in cell biology.Microsc Res Tech. 2011 Mar;74(3):251-6. doi: 10.1002/jemt.20898. Microsc Res Tech. 2011. PMID: 20623756
-
Applications and challenges of digital pathology and whole slide imaging.Biotech Histochem. 2015 Jul;90(5):341-7. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2015.1044566. Epub 2015 May 15. Biotech Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25978139 Review.
-
An overview of state-of-the-art image restoration in electron microscopy.J Microsc. 2018 Sep;271(3):239-254. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12716. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Microsc. 2018. PMID: 29882967 Review.
Cited by
-
Demodex folliculorum.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 15;15(12):1520. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121520. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564840 Free PMC article.
References
-
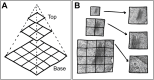
- Adelson, E., Anderson, C., Bergen, J., Burt, P. and Ogden, J. (1984). Pyramid Methods in Image Processing. RCA Engineer. 29, 33-41.
-
- Bhandari, M., Soria-Carrera, H., Wohlmann, J., Dal, N. K., De La Fuente, J. M., Martin-Rapun, R., Griffiths, G. and Fenaroli, F. (2023). Subcellular localization and therapeutic efficacy of polymeric micellar nanoparticles encapsulating bedaquiline for tuberculosis treatment in zebrafish. Biomater Sci. 11, 2103-2114. 10.1039/d2bm01835g - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bourgeois, C. A. and Hubert, J. (1988). Spatial relationship between the nucleolus and the nuclear envelope: structural aspects and functional significance. In International Review of Cytology (ed. Bourne G. H., Jeon K. W. and Friedlander M.), pp. 1-52. Academic Press. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

