Self-reported hearing loss is associated with faster cognitive and functional decline but not diagnostic conversion in the ADNI cohort
- PMID: 39324520
- PMCID: PMC11567835
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14252
Self-reported hearing loss is associated with faster cognitive and functional decline but not diagnostic conversion in the ADNI cohort
Abstract
Introduction: Hearing loss is identified as one of the largest modifiable risk factors for cognitive impairment and dementia. Studies evaluating this relationship have yielded mixed results.
Methods: We investigated the longitudinal relationship between self-reported hearing loss and cognitive/functional performance in 695 cognitively normal (CN) and 941 participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) enrolled in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
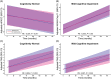
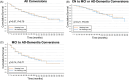
Results: Within CN participants with hearing loss, there was a significantly greater rate of cognitive decline per modified preclinical Alzheimer's cognitive composite. Within both CN and MCI participants with hearing loss, there was a significantly greater rate of functional decline per the functional activities questionnaire (FAQ). In CN and MCI participants, hearing loss did not significantly contribute to the risk of progression to a more impaired diagnosis.
Discussion: These results confirm previous studies demonstrating a significant longitudinal association between self-reported hearing loss and cognition/function but do not demonstrate an increased risk of conversion to a more impaired diagnosis.
Clinical trial registration information: NCT00106899 (ADNI: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, clinicaltrials.gov), NCT01078636 (ADNI-GO: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Grand Opportunity, clinicaltrials.gov), NCT01231971 (ADNI2: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 2, clinicaltrials.gov), NCT02854033 (ADNI3: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3, clinicaltrials.gov).
Highlights: Hearing loss is a potential modifiable risk factor for dementia. We assessed the effect of self-reported hearing loss on cognition and function in the ADNI cohort. Hearing loss contributes to significantly faster cognitive and functional decline. Hearing loss was not associated with conversion to a more impaired diagnosis.
Keywords: cognition; conversion; hearing loss; memory; neuropsychological testing.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
R.S.O. reports grants for clinical trials from Cognition Therapeutics and Bristol‐Myers Squibb outside of the submitted work. A.P.M. reports grants for clinical trials from Genentech, Eli Lilly, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. C.H.v.D. reports grants for clinical trials from Biogen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Merck, Eisai, Janssen, Roche, Genentech, Toyama, and Biohaven outside the submitted work. A.P.M., E.S.S., Y.Z., and C.H.v.D. report grant support from the NIH for work not related to this manuscript. C.H.v.D. reports consulting fees from Kyowa Kirin, Roche, Merck, Eli Lilly, and Janssen. A.P.M. received honoraria for presentations at University of Connecticut and Stanford University. R.S.O. received honoraria for presentations at University of Kansas. A.P.M. received support from ACTC/ATRI for travel to ACTC/ATRI meetings. A.P.M. is a member of the ISTAART Neuroimaging PIA executive committee. A.A.M. and S.W. have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures
References
-
- Ageing and Health . World Health Organization. 2022. [updated October 22nd 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/ageing‐and‐health
-
- 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(4):1598‐1695. - PubMed
-
- Dementia World Health Organization Website2023 [updated March 15th 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/news‐room/fact‐sheets/detail/dementia
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- P30AG021342/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GE Healthcare
- AbbVie, Alzheimer's Association
- P30AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- W81XWH-12-2-0012/Department of Defense
- EuroImmun
- Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC.
- Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- Servier
- Lumosity
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Piramal Imaging
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG068191/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI)
- Araclon Biotech
- U01 AG024904/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
- Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC.
- CereSpir, Inc.
- Northern California Institute for Research and Education
- BioClinica, Inc.
- RF1 AG081413/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021342/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Transition Therapeutics
- Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research &Development, LLC.
- Cogstate; Eisai Inc.
- the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering
- The Canadian Institutes of Health Research
- Pfizer Inc.
- Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- IXICO Ltd.
- NeuroRx Research
- RF1AG081413/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- RF1AG068191/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Neurotrack Technologies
- Fujirebio
- Lundbeck
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

