Increased intracellular H2S levels enhance iron uptake in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 39324809
- PMCID: PMC11481527
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01991-24
Increased intracellular H2S levels enhance iron uptake in Escherichia coli
Abstract
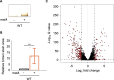
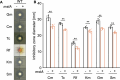
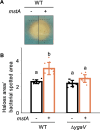
We investigated the impact of intracellular hydrogen sulfide (H2S) hyperaccumulation on the transcriptome of Escherichia coli. The wild-type (WT) strain overexpressing mstA, encoding 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase, produced significantly higher H2S levels than the control WT strain. The mstA-overexpressing strain exhibited increased resistance to antibiotics, supporting the prior hypothesis that intracellular H2S contributes to oxidative stress responses and antibiotic resistance. RNA-seq analysis revealed that over 1,000 genes were significantly upregulated or downregulated upon mstA overexpression. The upregulated genes encompassed those associated with iron uptake, including siderophore synthesis and iron import transporters. The mstA-overexpressing strain showed increased levels of intracellular iron content, indicating that H2S hyperaccumulation affects iron availability within cells. We found that the H2S-/supersulfide-responsive transcription factor YgaV is required for the upregulated expression of iron uptake genes in the mstA-overexpression conditions. These findings indicate that the expression of iron uptake genes is regulated by intracellular H2S, which is crucial for oxidative stress responses and antibiotic resistance in E. coli.
Importance: H2S is recognized as a second messenger in bacteria, playing a vital role in diverse intracellular and extracellular activities, including oxidative stress responses and antibiotic resistance. Both H2S and iron serve as essential signaling molecules for gut bacteria. However, the intricate intracellular coordination between them, governing bacterial physiology, remains poorly understood. This study unveils a close relationship between intracellular H2S accumulation and iron uptake activity, a relationship critical for antibiotic resistance. We present additional evidence expanding the role of intracellular H2S synthesis in bacterial physiology.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; YgaV; hydrogen sulfide; persulfide; reactive sulfur species; supersulfide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Nishida M, Sawa T, Kitajima N, Ono K, Inoue H, Ihara H, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M, Suematsu M, Kurose H, van der Vliet A, Freeman BA, Shibata T, Uchida K, Kumagai Y, Akaike T. 2012. Hydrogen sulfide anion regulates redox signaling via electrophile sulfhydration. Nat Chem Biol 8:714–724. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ono K, Akaike T, Sawa T, Kumagai Y, Wink DA, Tantillo DJ, Hobbs AJ, Nagy P, Xian M, Lin J, Fukuto JM. 2014. Redox chemistry and chemical biology of H2S, hydropersulfides, and derived species: implications of their possible biological activity and utility. Free Rad Biol Med 77:82–94. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.09.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mironov A, Seregina T, Nagornykh M, Luhachack LG, Korolkova N, Lopes LE, Kotova V, Zavilgelsky G, Shakulov R, Shatalin K, Nudler E. 2017. Mechanism of H2S-mediated protection against oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:6022–6027. doi:10.1073/pnas.1703576114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

