Effect of Anti-PEG Antibody on Immune Response of mRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles
- PMID: 39324825
- PMCID: PMC11539066
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00628
Effect of Anti-PEG Antibody on Immune Response of mRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles
Abstract
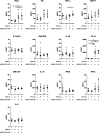
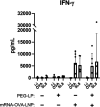
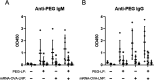
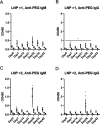
Lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated mRNA (mRNA-LNP) vaccines have been approved for use to combat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The mRNA-LNPs contain PEG-conjugated lipids. Clinical studies have reported that mRNA-LNPs induce the production of anti-PEG antibodies, but the anti-PEG antibodies do not affect the production of neutralizing antibodies. However, the detailed influence of anti-PEG antibodies on mRNA-LNP vaccines remains unclear. Therefore, in this study, we prepared ovalbumin (OVA) as a model antigen-encoding mRNA-loaded LNP (mRNA-OVA-LNP), and we determined whether anti-PEG antibodies could affect the antigen-specific immune response of mRNA-OVA-LNP vaccination in mice pretreated with PEG-modified liposomes to induce the production of anti-PEG antibodies. After intramuscular (i.m.) injection of the mRNA-LNP, the anti-PEG antibodies did not change the expression of protein or induction of cytokine and cellular immune response but did slightly increase the induction of antigen-specific antibodies. Furthermore, repeated mRNA-LNP i.m. injection induced the production of anti-PEG IgM and anti-PEG IgG. Our results suggest that mRNA-LNP induces the production of anti-PEG antibodies, but the priming of the antigen-specific immune response of mRNA-LNP vaccination is not notably affected by anti-PEG antibodies.
Keywords: anti-PEG antibody; lipid nanoparticle; mRNA; polyethylene glycol; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Y.Y. is an employee of the Research Foundation for Microbial Diseases of Osaka University.
Figures


References
-
- Chen B. M.; Su Y. C.; Chang C. J.; Burnouf P. A.; Chuang K. H.; Chen C. H.; Cheng T. L.; Chen Y. T.; Wu J. Y.; Roffler S. R. Measurement of Pre-Existing IgG and IgM Antibodies against Polyethylene Glycol in Healthy Individuals. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10661–10666. 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03109. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dams E. T.; Laverman P.; Oyen W. J.; Storm G.; Scherphof G. L.; van Der Meer J. W.; Corstens F. H.; Boerman O. C. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1071–1079. - PubMed
-
- Fix S. M.; Nyankima A. G.; McSweeney M. D.; Tsuruta J. K.; Lai S. K.; Dayton P. A. Accelerated Clearance of Ultrasound Contrast Agents Containing Polyethylene Glycol is Associated with the Generation of Anti-Polyethylene Glycol Antibodies. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1266–1280. 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.02.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

