Economic burden and quality of life of caregivers of patients with sickle cell disease in the United Kingdom and France: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39325265
- PMCID: PMC11427640
- DOI: 10.1186/s41687-024-00784-y
Economic burden and quality of life of caregivers of patients with sickle cell disease in the United Kingdom and France: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Sickle cell disease (SCD), a genetic blood disorder that affects red blood cells and oxygen delivery to body tissues, is characterized by haemolytic anaemia, pain episodes, fatigue, and end-organ damage with acute and chronic dimensions. Caring for patients with SCD imposes a high burden on informal caregivers. This study aims to capture the impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and economic burden of caregiving for patients with SCD.
Methods: Validated instruments of HRQoL (EQ-5D-5L, Carer Quality of Life-7 dimensions [CarerQol-7D]) and productivity (Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Specific Health Problem [WPAI: SHP]) were administered via a cross-sectional online survey to caregivers in the United Kingdom (UK) and France. Demographics, HRQoL, and economic burden data were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Economic burden was determined using country-specific minimum and average wage values. Subgroup analysis examined caregivers with and without SCD.
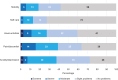
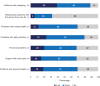
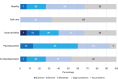
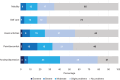
Results: Sixty-nine caregivers were recruited (UK, 43; France, 26), 83% were female, and 22% had SCD themselves. The mean (SD) caregiver EQ-5D-5L score was 0.66 (0.28) (UK, 0.62; France, 0.73), and the mean CarerQol-7D score was 80.69 (24.40) (UK, 78.72 [25.79]; France, 83.97 [22.01]). Mental health problems were reported in 72% and 70% of caregivers measured using the EQ-5D-5L and CarerQol-7D, respectively. Financial problems were reported by 68% of caregivers, with mean annual minimum wage productivity losses of £4209 and €3485, increasing to £5391 and €9319 for average wages. Sensitivity analysis determined additional HRQoL decrements for caregivers with and without, SCD.
Conclusion: Caring for patients with SCD impacts the HRQoL and economic burden of caregivers. Further research to support the complex needs of SCD caregivers is required.
Keywords: Caregiver burden; HRQoL; Health-related quality of life; Productivity loss; SCD; Sickle cell disease.
Plain language summary
Caregivers play an important role in the lives of the people with sickle cell disease that they care for; however, their mental and physical health and their finances can be affected, particularly if their ability to work is impacted. The extent to which caring for a person with sickle cell disease impacts caregivers is not fully understood. In this study, 69 caregivers of a family member, partner, or friend with sickle cell disease in the United Kingdom or France completed an online survey to share their experiences about how caring for someone with sickle cell disease can impact a caregiver’s quality of life and financial well-being. Caregiving negatively affected the quality of life of caregivers compared with people in the general population and caused a large financial and social burden. Around 70% of caregivers reported having mental health problems, 68% reported financial problems, and lost work hours and lost income were not uncommon. More research is needed to understand the specific needs of caregivers of people with sickle cell disease and how best to support them.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Financial interests: MB received support from Novartis in the form of travel grants and support for a clinical service as well as advisory boards. Octapharma advisory board, Terumo honorarium and support for a patient event, Global Blood Therapeutics advisory board, Hemeo advisory board, Pfizer honorarium and educational support, Forte advisory board, Primeglobal honorarium, Agios advisory board and support for a patient event. SB, YO, and LL are full-time employees of Putnam PHMR. GTB is a full-time employee and equity ownership of Pfizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life and productivity burden for non-professional caregivers of adults with rare diseases: a real-world study.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Jun 6;20(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03796-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40481583 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life study for caregivers of people with uncontrolled focal-onset seizures.J Med Econ. 2022 Jan-Dec;25(1):66-76. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2021.2018871. J Med Econ. 2022. PMID: 34906033
-
Self-reported burden of caregiver of adults with depression: a cross-sectional study in five Western European countries.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Jun 21;21(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03255-6. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34154555 Free PMC article.
-
[Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French.
-
Caregiver Burden of Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Systematic Review.Pharmacoeconomics. 2023 Mar;41(3):275-293. doi: 10.1007/s40273-022-01197-9. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Pharmacoeconomics. 2023. PMID: 36515815
Cited by
-
Financial health and well-being of rural female caregivers of older adults with chronic illnesses.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Apr 10;25(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-05853-5. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40211160 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to ready-to-use therapeutic food in older children with sickle cell anaemia and severe acute malnutrition: a mixed-methods study in a low-income setting.BMJ Glob Health. 2025 Aug 7;10(8):e019096. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2025-019096. BMJ Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40780831 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Sedrak A, Kondamudi NP (2021) Sickle cell disease. StatPearls Publishing, In StatPearls [Internet] - PubMed
-
- NICE clinical knowledge summaries (2022), July 20 How common is sickle cell disease? https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/sickle-cell-disease/background-informatio.... Accessed 10 Nov 2022
-
- National Health Service (2019) Overview: Sickle cell disease. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/sickle-cell-disease/. Accessed 21 Nov 2022
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

