Extra-osseous Roles of the RANK-RANKL-OPG Axis with a Focus on Skeletal Muscle
- PMID: 39325366
- PMCID: PMC11499344
- DOI: 10.1007/s11914-024-00890-2
Extra-osseous Roles of the RANK-RANKL-OPG Axis with a Focus on Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
Purpose of review: This review aims to consolidate recent observations regarding extra-osseous roles of the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis, primarily within skeletal muscle.
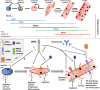
Recent findings: Preclinical efforts to decipher a common signalling pathway that links the synchronous decline in bone and muscle health in ageing and disease disclosed a potential role of the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis in skeletal muscle. Evidence suggests RANKL inhibition benefits skeletal muscle function, mass, fibre-type switching, calcium homeostasis and reduces fall incidence. However, there still exists ambiguity regarding the exact mechanistic actions and subsequent functional improvements. Other potential RANK-RANKL-OPG extra-osseous roles include regulation of neural-inflammation and glucose metabolism. Growing evidence suggests the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis may play a regulatory role in extra-osseous tissues, especially in skeletal muscle. Targeting RANKL may be a novel therapy in ameliorating loss of muscle mass and function. More research is warranted to determine the causality of the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis in extra-osseous tissues, especially those affected by aging.
Keywords: Denosumab; Extra-osseous; NF-κB signalling; Osteoprotegerin; RANK-RANKL-OPG axis; Skeletal muscle.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors J.G., K.G-W., I.B. and N.B. declare no competing interests. P.K.: Consultant to Mesentech, Septerna, Nimbus, UCB, Amgen, Radius Health, Agnovos, Ascendis, Ashi Bio, and NextCure. E.M.: Consultant/Advisor/Speaker for Amgen, Fresenius Kabi, Internis, ObsEva, Theramex, UCB. Financial holdings – None.
Figures

References
-
- Takayanagi H. RANKL as the master regulator of osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):13–8. 10.1007/s00774-020-01191-1. - PubMed
-
- McGonigle JS, Giachelli CM, Scatena M. Osteoprotegerin and RANKL differentially regulate angiogenesis and endothelial cell function. Angiogenesis. 2008;12(1):35–46. 10.1007/s10456-008-9127-z. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

