Tongxinluo and Functional Outcomes Among Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 39325453
- PMCID: PMC11428006
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33463
Tongxinluo and Functional Outcomes Among Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Previous studies revealed limited effectiveness of neuroprotective agents in treating acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Tongxinluo, developed from traditional Chinese medicines, has been recognized as a novel neuroprotective agent with anti-inflammatory properties that stabilize vulnerable plaques in animal models and patients with myocardial infarction.
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of Tongxinluo in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
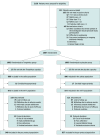
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter, open-label, double-blind, randomized clinical trial included 2007 patients with AIS and a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 4 and 22 at admission. The trial was conducted at 50 hospitals in China from March 1, 2014, to October 31, 2016. Data were analyzed from November 14, 2016, to November 16, 2017.
Interventions: Eligible patients were randomized within 72 hours of symptom onset to the Tongxinluo group or the control group. Participants received 4 oral capsules of Tongxinluo or placebo, 3 times a day for 90 days. Other treatment was administrated according to guidelines.
Main outcomes and measure: The primary outcome was a favorable functional outcome at day 90 after randomization, defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0 to 1 (on a scale of 0 [no neurologic deficit, no symptoms, or completely recovered] to 6 [death]). All statistical analyses were performed in a modified intention-to-treat population, defined as all patients who underwent randomization, were given any treatment, and underwent any posttreatment assessment.
Results: Among 2007 patients with AIS who were randomized, 1946 (96.5%) were included in the modified intention-to-treat analysis (973 in the Tongxinluo group and 973 in the control group, with mean [SD] age of 60.5 [9.2] years and 1342 [69.0%] male). Patients in the Tongxinluo group had a significantly higher proportion of favorable functional outcomes at day 90 compared with those in the control group (mRS score of 0-1, 640 [65.8%] vs 575 [59.1%]; odds ratio, 1.33 [95% CI, 1.11-1.60]; P = .002). The prespecified subgroup analyses indicated that, among all subgroups, additional Tongxinluo treatment had similar outcomes.
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with ischemic stroke within 72 hours after symptom onset, those additionally receiving Tongxinluo were more likely to have a favorable functional outcome, compared with a placebo group. Further research in patients with thrombolysis and endovascular treatment are needed to explore these outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01919671.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Chang L, Hu L, Wei C, Zhang H, Liu S. Chinese medicine Tongxinluo capsule protects against blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke by inhibiting the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 pathway in mice. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29(9):105071. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105071 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

