Linear poly-ubiquitin remodels the proteome and influences hundreds of regulators in Drosophila
- PMID: 39325835
- PMCID: PMC11540324
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae209
Linear poly-ubiquitin remodels the proteome and influences hundreds of regulators in Drosophila
Abstract
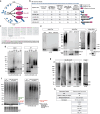
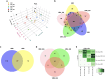
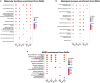
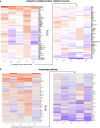
Ubiquitin controls many cellular processes via its posttranslational conjugation onto substrates. Its use is highly variable due to its ability to form poly-ubiquitin chains with various topologies. Among them, linear chains have emerged as important regulators of immune responses and protein degradation. Previous studies in Drosophila melanogaster found that expression of linear poly-ubiquitin that cannot be dismantled into single moieties leads to their ubiquitination and degradation or, alternatively, to their conjugation onto proteins. However, it remains largely unknown which proteins are sensitive to linear poly-ubiquitin. To address this question, here we expanded the toolkit to modulate linear chains and conducted ultra-deep coverage proteomics from flies that express noncleavable, linear chains comprising 2, 4, or 6 moieties. We found that these chains regulate shared and distinct cellular processes in Drosophila by impacting hundreds of proteins, such as the circadian factor Cryptochrome. Our results provide key insight into the proteome subsets and cellular pathways that are influenced by linear poly-ubiquitin chains with distinct lengths and suggest that the ubiquitin system is exceedingly pliable.
Keywords: autophagy; catabolism; genetics; immune system; proteasome; proteomics.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The author(s) declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Linear ubiquitin chains remodel the proteome and influence the levels of hundreds of regulators in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 10:2024.05.09.593206. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.09.593206. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Nov 6;14(11):jkae209. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae209. PMID: 38766269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Linear ubiquitin chains remodel the proteome and influence the levels of hundreds of regulators in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 10:2024.05.09.593206. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.09.593206. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Nov 6;14(11):jkae209. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae209. PMID: 38766269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Expression and Regulation of Deubiquitinase-Resistant, Unanchored Ubiquitin Chains in Drosophila.Sci Rep. 2018 May 31;8(1):8513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26364-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29855490 Free PMC article.
-
UbcD1 regulates Hedgehog signaling by directly modulating Ci ubiquitination and processing.EMBO Rep. 2017 Nov;18(11):1922-1934. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643289. Epub 2017 Sep 8. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887318 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of ubiquitin signaling and chain topology cross-talk.J Proteomics. 2020 Mar 20;215:103634. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103634. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31918034 Review.
-
Exploring the Rampant Expansion of Ubiquitin Proteomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1844:345-362. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8706-1_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30242720 Review.
Cited by
-
The ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2D maintains a youthful proteome and ensures protein quality control during aging by sustaining proteasome activity.PLoS Biol. 2025 Jan 29;23(1):e3002998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002998. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 39879147 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
