Combination of bortezomib and venetoclax targets the pro-survival function of LMP-1 and EBNA-3C of Epstein-Barr virus in spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines
- PMID: 39325843
- PMCID: PMC11481030
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012250
Combination of bortezomib and venetoclax targets the pro-survival function of LMP-1 and EBNA-3C of Epstein-Barr virus in spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines
Abstract
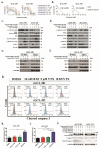
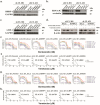
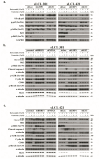
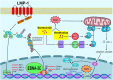
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) manipulates the ubiquitin-proteasome system and regulators of Bcl-2 family to enable the persistence of the virus and survival of the host cells through the expression of viral proteins in distinct latency patterns. We postulate that the combination of bortezomib (proteasome inhibitor) and venetoclax (Bcl-2 inhibitor) [bort/venetoclax] will cause synergistic killing of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) through targeting the pro-survival function of latent viral proteins such as latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) and EBV nuclear antigen-3C (EBNA-3C). Bort/venetoclax could synergistically kill spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines (sLCLs) derived from patients with PTLD and EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis by inducing DNA damage response, apoptosis and G1-S cell cycle arrest in a ROS-dependent manner. Bortezomib potently induced the expression of Noxa, a pro-apoptotic initiator and when combined with venetoclax, inhibited Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 simultaneously. Bortezomib prevented LMP-1 induced proteasomal degradation of IκBα leading to the suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Bortezomib also rescued Bcl-6 from EBNA-3C mediated proteasomal degradation thus maintaining the repression of cyclin D1 and Bcl-2 causing G1-S arrest and apoptosis. Concurrently, venetoclax inhibited Bcl-2 upregulated by either LMP-1 or EBNA-3C. Bort/venetoclax decreased the expression of phosphorylated p65 and Bcl-2 at serine 70 thereby suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting apoptosis, respectively. These data corroborated the marked suppression of the growth of xenograft of sLCL in SCID mice (p<0.001). Taken together, the combination of bortezomib and venetoclax targets the pro-survival function of LMP-1 and EBNA-3C of Epstein-Barr virus in spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines.
Copyright: © 2024 Tam et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of LMP and EBNA genes in Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas in Hu-PBL/SCID mice.Oncol Rep. 2016 Feb;35(2):905-11. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4401. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26548532
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of venetoclax, a BCL2 inhibitor, in systemic chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease.Sci Rep. 2025 May 27;15(1):18569. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03719-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40425709 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of SAHA and bortezomib up-regulates CDKN2A and CDKN1A and induces apoptosis of Epstein-Barr virus-positive Wp-restricted Burkitt lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines.Br J Haematol. 2014 Dec;167(5):639-50. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13089. Epub 2014 Aug 25. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 25155625
-
Therapeutic Strategies against Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Cancers Using Proteasome Inhibitors.Viruses. 2017 Nov 21;9(11):352. doi: 10.3390/v9110352. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29160853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

