Shared fate was associated with sustained cooperation during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 39325844
- PMCID: PMC11426462
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307829
Shared fate was associated with sustained cooperation during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
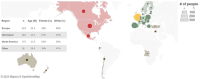
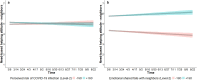
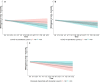
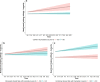
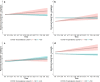
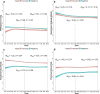
Did the COVID-19 pandemic bring people together or push them apart? While infectious diseases tend to push people apart, crises can also bring people together through positive interdependence. We studied this question by asking an international sample (N = 1,006) about their inclinations to cooperate, perceptions of interdependence (i.e., shared fate), and perceived risk as well as local prevalence of COVID-19 infection across 14 time points from March to August, 2020. While perceived interdependence with others tended to increase during this time period, inclinations to cooperate decreased over time. At the within-person level, higher local prevalence of COVID-19 attenuated increases in perceived interdependence with others, and was associated with lower inclinations to cooperate. At the between-person level, people with high perceived interdependence with others reported more stable, or increasing, inclinations to cooperate over time than people with low perceived interdependence. Establishing a high sense of perceived interdependence with others may thus allow people to maintain cooperation during crises, even in the face of challenging circumstances such as those posed by a highly transmissible virus.
Copyright: © 2024 Guevara Beltran et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Berrebi C, Karlinsky A, Yonah H. Individual and community behavioral responses to natural disasters. Nat Hazards. 2021;105: 1541–69. 10.1007/s11069-020-04365-2 - DOI
-
- Andrighetto L, Vezzali L, Bergamini G, Nadi C, Giovannini D. Inside the earthquake: Perceived disaster exposure and helping intentions among Italian and immigrant victims of the 2012 Italian earthquakes. Group Process Intergroup Relat. 2016;19: 753–68. 10.1177/1368430215591040 - DOI
-
- Drury J, Brown R, González R, Miranda D. Emergent social identity and observing social support predict social support provided by survivors in a disaster: Solidarity in the 2010 Chile earthquake. Eur J Soc Psychol. 2016;46: 209–23. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ejsp.2146 - DOI
-
- Guevara Beltran D, Whisner CM, Krems JA, Todd PM, Aktipis A. Food scarcity and disease concern reduce interdependence when people eat together. Eur J Soc Psychol. 2023; 53: 1245–1261. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ejsp.2972 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

