A kalihinol analog disrupts apicoplast function and vesicular trafficking in P. falciparum malaria
- PMID: 39325875
- PMCID: PMC11793105
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adm7966
A kalihinol analog disrupts apicoplast function and vesicular trafficking in P. falciparum malaria
Abstract
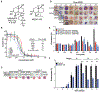
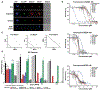
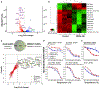
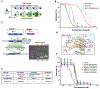
We report the discovery of MED6-189, an analog of the kalihinol family of isocyanoterpene natural products that is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum strains, blocking both asexual replication and sexual differentiation. In vivo studies using a humanized mouse model of malaria confirm strong efficacy of the compound in animals with no apparent hemolytic activity or toxicity. Complementary chemical, molecular, and genomics analyses revealed that MED6-189 targets the parasite apicoplast and acts by inhibiting lipid biogenesis and cellular trafficking. Genetic analyses revealed that a mutation in PfSec13, which encodes a component of the parasite secretory machinery, reduced susceptibility to the drug. Its high potency, excellent therapeutic profile, and distinctive mode of action make MED6-189 an excellent addition to the antimalarial drug pipeline.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
A Potent Kalihinol Analogue Disrupts Apicoplast Function and Vesicular Trafficking in P. falciparum Malaria.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 22:2023.11.21.568162. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.21.568162. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Science. 2024 Sep 27;385(6716):eadm7966. doi: 10.1126/science.adm7966. PMID: 38045341 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization, World Malaria Report 2023 (World Health Organization, 2023).
-
- World Health Organization, Global Report on Antimalarial Drug Efficacy and Drug Resistance: 2000–2010 (World Health Organization, 2010).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 TW010496/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AI136118/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI153100/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123321/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI138139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI152220/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI142743/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R43 AI136118/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI136511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- INV-031788/GATES/Gates Foundation/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

