Neuroprotective Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Acute Stroke
- PMID: 39326864
- PMCID: PMC11471356
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2024.01529
Neuroprotective Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Acute Stroke
Conflict of interest statement
FC has received travel grants and/or speaking honoraria from Biogen, Merck, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Roche and research grants from Merck, which are not relevant to this work. AZ reported consultancies with Bayer, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and CSL Behring, which were not relevant to this work. RC owns shares in IGEA. SSa and SSe are employees of IGEA.
The other authors have no conflicting interests to declare.
Figures
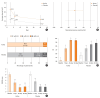
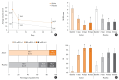
References
-
- Chamorro Á, Dirnagl U, Urra X, Planas AM. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:869–881. - PubMed
-
- Borea PA, Gessi S, Merighi S, Varani K. Adenosine as a multisignalling guardian angel in human diseases: when, where and how does it exert its protective effects? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37:419–434. - PubMed
-
- Capone F, Salati S, Vincenzi F, Liberti M, Aicardi G, Apollonio F, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields: a novel attractive therapeutic opportunity for neuroprotection after acute cerebral ischemia. Neuromodulation. 2022;25:1240–1247. - PubMed
-
- Melani A, Corti F, Cellai L, Vannucchi MG, Pedata F. Low doses of the selective adenosine A2A receptor agonist CGS21680 are protective in a rat model of transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2014;1551:59–72. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

