Finite element analysis in the Dental Sciences: A Bibliometric and a Visual Study
- PMID: 39327150
- PMCID: PMC11976560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.08.005
Finite element analysis in the Dental Sciences: A Bibliometric and a Visual Study
Abstract
Introduction and aims: Finite element analysis (FEA) is an incrementally practical and precise tool for the prediction of stress effects on different tissue structures and has therefore interested dental researchers for decades. This bibliometric and visualized study was aimed to assess the research progress related to FEA in the dental sciences in terms of research trends and frontiers.
Methods: The articles about FEA studies in this field during 1999 to 2024 were obtained from Web of Science Core Collection. Then, these results were analysed and plotted using Microsoft Excel, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace in order to find out the historical evolution, current hotspots, and future directions.
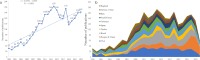
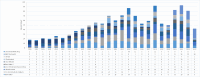
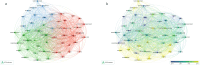
Results: Total 2838 literature records related to the topic were retrieved from Web of Science Core Collection. The most active country and institution were USA (538 documents) and Universidade Estadual Paulista (140 documents), respectively. Baggi et al from University of Naples Federico II was the author with the most highly cited article (352 citations), which was published on the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry in 2008. Dental Materials ranked first (231 documents) among the 10 journals with the greatest numbers of relevant publications. The top three trending keywords were 'dental implant', 'stress distribution', and 'fracture'. The endocrown, clear aligner, and posterior edentulism were scientific frontiers in this field.
Conclusion: The present study provides a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research in the dental science by FEA approaches, which will identify active hotspots of scientific interest to guide further research endeavours.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Biomechanics; Decision-making; Dental practice; Dental stress analysis; Finite element analysis.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research hotspots and trends of bone defects based on Web of Science: a bibliometric analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Oct 8;15(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01973-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33032636 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Scientific mapping of hotspots and trends of post and core research based on the Web of Science: A bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 19;10(1):e23786. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23786. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38226214 Free PMC article.
-
Global Trends and Research Hotspots of Exercise for Intervening Diabetes: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 7;10:902825. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.902825. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35875005 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the evolution of placental oxidative stress research from a bibliometric perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1475244. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475244. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39484166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Finite Element Analysis of Functionally Loaded Subperiosteal Implants Evaluated on a Realistic Model Reproducing Severe Atrophic Jaws.Methods Protoc. 2025 Jan 18;8(1):8. doi: 10.3390/mps8010008. Methods Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39846694 Free PMC article.
-
Loading Pressure Induced by 4 mm Implants on the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: A 3D Finite Element Analysis Model.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 7;14(7):2535. doi: 10.3390/jcm14072535. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40217984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpegna G., Alovisi M., Paolino D.S., et al. Evaluation of pressure distribution against root canal walls of NiTi rotary instruments by finite element analysis. Appl Sci (Basel) 2020;10(8):2981. doi: 10.3390/app10082981. - DOI
-
- Baggi L., Cappelloni I., Di Girolamo M., Maceri F., Vairo G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2008;100(6):422–431. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3913(08)60259-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

