The role of nonmyocardial cells in the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the protective effects of FGF21: a current understanding
- PMID: 39327594
- PMCID: PMC11426003
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01842-0
The role of nonmyocardial cells in the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the protective effects of FGF21: a current understanding
Abstract
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) represents a unique myocardial disease originating from diabetic metabolic disturbances that is characterized by myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction. While recent research regarding the pathogenesis and treatment of DCM has focused primarily on myocardial cells, nonmyocardial cells-including fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), endothelial cells (ECs), and immune cells-also contribute significantly to the pathogenesis of DCM. Among various therapeutic targets, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been identified as a promising agent because of its cardioprotective effects that extend to nonmyocardial cells. In this review, we aim to elucidate the role of nonmyocardial cells in DCM and underscore the potential of FGF21 as a therapeutic strategy for these cells.
Keywords: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Nonmyocardial cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

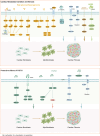

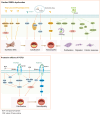

References
-
- Schleicher E, Gerdes C, Petersmann A, Müller-Wieland D, Müller UA, Freckmann G, et al. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022;130:S1-8. - PubMed
-
- Atlas D. International diabetes federation. In: IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th edn. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation. 2015. p. 33.
-
- Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1972;30:595–602. - PubMed
-
- Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ. Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes. 2002;51:1938–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFS0630/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2022YFS0627/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2022YFS0578/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- U23A20398/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022ZYD0057/The Central Government Guides Local Science and Technology Development Project
- 2024NSFSC0580/Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
- 2021YJ0200/Applied Basic Research Program of Sichuan Province
- 2023NSFSC1840/Applied Basic Research Program of Sichuan Province
- 2022YFS0627-A1/Science and Technology Project of Luzhou Government
- 2022YFS0630-B1/Science and Technology Project of Luzhou Government
- 2021ZKMS005/Southwest Medical University
- 2022QN013/Southwest Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

