Spatial distribution of teenage pregnancy and its associated factors in Ethiopia: spatial and multilevel analysis of EDHS 2019
- PMID: 39327596
- PMCID: PMC11426100
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-024-01380-8
Spatial distribution of teenage pregnancy and its associated factors in Ethiopia: spatial and multilevel analysis of EDHS 2019
Abstract
Background: One of the reasons for the high rates of maternal and child morbidity and mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa is the rising proportion of teenage pregnancy. Preventing teenage pregnancy is critical to meeting sustainable development goal number three which aims to reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. To support the achievement of this goal, this study aimed to assess the spatial variation and factors associated with teenage pregnancy in Ethiopia using the recent nationally representative data.
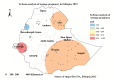
Methods: A secondary data analysis of the 2019 Ethiopian mini Demographic and Health Survey was conducted with a total weighted sample of 2211 (unweighted 2100) teenagers. The Bernoulli model was fitted using SaTScan version 9.6 to identify hotspot areas and the geospatial pattern and prediction of teenage pregnancy were mapped using ArcGIS version 10.7. A multilevel logistic regression model was fitted to identify factors associated with teenage pregnancy among teenagers. Adjusted OR with 95% CI was calculated and variables having a p-value less than 0.05 were statistically significant factors of teenage pregnancy.
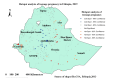
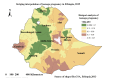
Result: The prevalence of teenage pregnancy among adolescents aged 15-19 years in Ethiopia was 12.89% (95% CI: 11.56%, 14.36%). The SaTScan analysis identified a primary cluster in the Gambella region of Ethiopia (log-likelihood ratio = 14.02, p < 0.001). A high prevalence of teenage pregnancy was observed in Somalia, Afar, Gambella, and the southern part of the Oromia regions of Ethiopia. Age, educational status- primary and secondary, religion- protestant, having television, contraceptive knowledge, household head-female, and region- Small peripheral were significant determinants of teenage pregnancy.
Conclusion: The spatial distribution of teenage pregnancy in Ethiopia was nonrandom. Age, educational status, religion, having television, contraceptive knowledge, sex of household head, and region were significant determinants of teenage pregnancy. Therefore, concerned government bodies and other stakeholders should organize periodic educational campaigns and youth-friendly reproductive health services. Collaboration between healthcare professionals, and religious and community leaders could also form a strategic partnership that makes interventions more comprehensive, culturally sensitive, and effective in reducing teenage pregnancy.
Keywords: EDHS; Ethiopia; Multilevel analysis; Spatial analysis; Teenage pregnancy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial distribution and determinants of abortion among reproductive age women in Ethiopia, evidence from Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey 2016 data: Spatial and mixed-effect analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 29;15(6):e0235382. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235382. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32598398 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and community-level determinants, and spatial distribution of institutional delivery in Ethiopia, 2016: Spatial and multilevel analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 12;15(11):e0242242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242242. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33180845 Free PMC article.
-
A multiscale geographically weighted regression analysis of teenage pregnancy and associated factors among adolescents aged 15 to 19 in Ethiopia using the 2019 mini-demographic and health survey.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0310025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310025. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240994 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic variation and associated factors of long-acting contraceptive use among reproductive-age women in Ethiopia: a multi-level and spatial analysis of Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey 2016 data.Reprod Health. 2021 Jun 10;18(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01171-2. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 34112194 Free PMC article.
-
Applied nutritional investigation spatial variation and determinants of stunting among children aged less than 5 y in Ethiopia: A spatial and multilevel analysis of Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey 2019.Nutrition. 2022 Nov-Dec;103-104:111786. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2022.111786. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Nutrition. 2022. PMID: 35970098 Review.
References
-
- Organization WH, Adolscent pregnancy. 2022 [cited 2023 January 26]; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/adolescent-pregnancy
-
- Neal S, et al. Childbearing in adolescents aged 12–15 years in low resource countries: a neglected issue. New estimates from demographic and household surveys in 42 countries. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2012;91(9):1114–8. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Adolescent pregnancy. 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

