Vitamin D3 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain via Suppression of Mitochondria-Associated Ferroptosis by Inhibiting PKCα/NOX4 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 39328008
- PMCID: PMC11427799
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70067
Vitamin D3 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain via Suppression of Mitochondria-Associated Ferroptosis by Inhibiting PKCα/NOX4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Aims: Neuropathic pain remains a significant unmet medical challenge due to its elusive mechanisms. Recent clinical observations suggest that vitamin D (VitD) holds promise in pain relief, yet its precise mechanism of action is still unclear. This study explores the therapeutical role and potential mechanism of VitD3 in spared nerve injury (SNI)-induced neuropathic pain rat model.
Methods: The analgesic effects and underlying mechanisms of VitD3 were evaluated in SNI and naïve rat models. Mechanical allodynia was assessed using the Von Frey test. Western blotting, immunofluorescence, biochemical assay, and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were employed to investigate the molecular and cellular effects of VitD3.
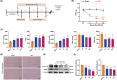
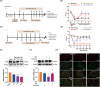
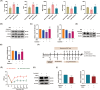
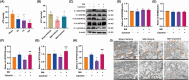
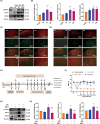
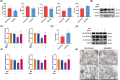
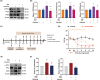
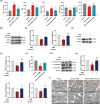
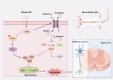
Results: Ferroptosis was observed in the spinal cord following SNI. Intrathecal administration of VitD3, the active form of VitD, activated the vitamin D receptor (VDR), suppressed ferroptosis, and alleviated mechanical nociceptive behaviors. VitD3 treatment preserved spinal GABAergic interneurons, and its neuroprotective effects were eliminated by the ferroptosis inducer RSL3. Additionally, VitD3 mitigated aberrant mitochondrial morphology and oxidative metabolism in the spinal cord. Mechanistically, VitD3 inhibited SNI-induced activation of spinal PKCα/NOX4 signaling. Inhibition of PKCα/NOX4 signaling alleviated mechanical pain hypersensitivity, accompanied by reduced ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in SNI rats. Conversely, activation of PKCα/NOX4 signaling in naïve rats induced hyperalgesia, ferroptosis, loss of GABAergic interneurons, and mitochondrial dysfunction in the spinal cord, all of which were reversed by VitD3 treatment.
Conclusions: Our findings provide evidence that VitD3 attenuates neuropathic pain by preserving spinal GABAergic interneurons through the suppression of mitochondria-associated ferroptosis mediated by PKCα/NOX4 signaling, probably via VDR activation. VitD, alone or in combination with existing analgesics, presents an innovative therapeutic avenue for neuropathic pain.
Keywords: GABAergic interneurons; PKCα/NOX4 signaling; ferroptosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; neuropathic pain; vitamin D3.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Mfn2 Contributes to Chronic Postsurgical Pain via Inducing the Pyroptosis of GABAergic Neurons in the Spinal Cord.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70508. doi: 10.1111/cns.70508. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40631358 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 2A as a Therapeutic Target for Relieving Mechanical Allodynia and Modulating Microglial Polarization in Neuropathic Pain Models Following Spinal Cord Injury.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jul 16;16(14):2629-2638. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00169. Epub 2025 Jun 28. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40580118
-
Heat Shock Protein 22 Attenuates Nerve Injury-induced Neuropathic Pain Via Improving Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Reducing Oxidative Stress Mediated By Spinal AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway in Male Rats.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 6;19(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10100-6. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38319409
-
Tramadol for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 15;6(6):CD003726. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003726.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28616956 Free PMC article.
-
Venlafaxine for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 23;2015(8):CD011091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26298465 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Precision Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury: Integrating CRISPR Technologies, AI-Driven Therapeutics, Single-Cell Omics, and System Neuroregeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 20;26(14):6966. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146966. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 1;26(7):3269. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073269. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244129 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Mfn2 Contributes to Chronic Postsurgical Pain via Inducing the Pyroptosis of GABAergic Neurons in the Spinal Cord.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70508. doi: 10.1111/cns.70508. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40631358 Free PMC article.
-
Nitroxidative Stress, Cell-Signaling Pathways, and Manganese Porphyrins: Therapeutic Potential in Neuropathic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;26(5):2050. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052050. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meisner J. G., Marsh A. D., and Marsh D. R., “Loss of GABAergic Interneurons in Laminae I–III of the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn Contributes to Reduced GABAergic Tone and Neuropathic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury,” Journal of Neurotrauma 27, no. 4 (2010): 729–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

