Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators Leading to Liver Injury: A Case Report
- PMID: 39328701
- PMCID: PMC11426965
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.67958
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators Leading to Liver Injury: A Case Report
Abstract
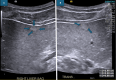
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) have gained popularity for their alleged ability to selectively target androgen receptors, potentially offering muscle-building benefits with fewer side effects than traditional steroids. However, the safety profile of SARMs, including RAD-140, is not fully understood. This case report presents a 29-year-old male who developed liver injury after taking RAD-140. The patient experienced jaundice and elevated liver enzymes after three months of RAD-140 use. A liver ultrasound revealed hepatic steatosis and a hyperechoic lesion. Symptoms resolved after discontinuing RAD-140. Similar cases of liver injury associated with RAD-140 have been reported, highlighting the potential hepatotoxicity of this SARM. Discontinuation of RAD-140 appears to reverse liver injury, but the long-term effects and risks of SARM use remain unclear. This case highlights the need for caution and monitoring when considering SARMs for performance enhancement.
Keywords: drug-induced liver injury; liver cirrhosis; rad-140; sarms; testalone.
Copyright © 2024, Demangone et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Athlete Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators Abuse: A Systematic Review.Am J Sports Med. 2025 Mar;53(4):999-1009. doi: 10.1177/03635465241252435. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Am J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 39755947
-
RAD-140 Drug-Induced Liver Injury.Ochsner J. 2022 Winter;22(4):361-365. doi: 10.31486/toj.22.0005. Ochsner J. 2022. PMID: 36561105 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs)-Induced Liver Injury: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Cureus. 2023 Feb 17;15(2):e35094. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35094. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36945289 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Induced Liver Injury Secondary to Enobosarm: A Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator.J Med Cases. 2022 May;13(5):244-248. doi: 10.14740/jmc3937. Epub 2022 May 7. J Med Cases. 2022. PMID: 35655632 Free PMC article.
-
Selective androgen receptor modulator use and related adverse events including drug-induced liver injury: Analysis of suspected cases.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Feb;80(2):185-202. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03592-3. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38059982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical assessment of the selective androgen receptor modulator RAD140 to increase muscle mass and bone mineral density.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jul;13(14):e70463. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70463. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40680216 Free PMC article.
-
Silent Threats to the Liver: Acute Hepatotoxicity Attributed to Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs).Cureus. 2025 Jun 7;17(6):e85500. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85500. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40625511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarmscombo: Www.sarmscombo.com. What are SARMS? 2024. https://sarmscombo.com/ https://sarmscombo.com/
-
- The global epidemiology of anabolic-androgenic steroid use: a meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Sagoe D, Molde H, Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Pallesen S. Ann Epidemiol. 2014;24:383–398. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources