Mental health literacy and help-seeking intention among Chinese elite athletes: the mediating roles of stigma and social support
- PMID: 39328811
- PMCID: PMC11424532
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1332343
Mental health literacy and help-seeking intention among Chinese elite athletes: the mediating roles of stigma and social support
Abstract
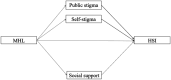
Objectives: Considering the importance of mental health help-seeking, researchers have closely examined the relationship between mental health literacy (MHL) and help-seeking intention (HSI). Furthermore, the high impact of stigma and the potential value of social support on HSI have been recognised. However, the relationship between these variables has not been fully tested within the context of Chinese elite athletes. This study addressed this gap by examining the relationship between MHL and HSI. Furthermore, it explored the mediating effects of public stigma, self-stigma, and social support on the relationship between MHL and HSI among Chinese elite athletes.
Methods: 450 Chinese elite athletes (M age = 18.12, SD = 3.20, 46.2% female) self-reported their MHL, public stigma, self-stigma, social support, and HSI. Mediation analysis was conducted using the bootstrap approach of the PROCESS macro version 3.3 of SPSS 25.
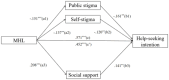
Results: The results showed a significant positive correlation between MHL and HSI (r = 0.348). The results also demonstrated that MHL was a predictor of HSI (β = 0.337, 95%CI [0.249, 0.425], p < 0.001). Furthermore, 1) the indirect effect of MHL → public stigma→HSI was 0.024 and a 95%CI [0.003, 0.053]. Specifically, MHL predicted public stigma (Estimate = -0.151, 95%CI [-0.187, -0.045], p < 0.001), and public stigma predicted HSI (Estimate = -0.161, 95%CI [- 0.549, -0.164], p < 0.001); 2) the indirect effect of MHL → self-stigma→ HSI was 0.016 and 95%CI [0.002, 0.038]. Specifically, MHL predicted self-stigma (Estimate = -0.137, 95%CI [-0.069, -0.013], p < 0.01), and self-stigma predicted HSI (Estimate = -0.120, 95%CI [-1.181, -0.186], p < 0.01); as well as 3) the indirect effect of MHL → social support→HSI was 0.029 and a 95%CI [0.009, 0.055]. Specifically, MHL predicted social support (Estimate = 0.208, 95%CI [0.018, 0.047], p < 0.001), and social support predicted HSI (Estimate = 0.141, 95%CI [0.578, 2.442], p < 0.01). Additionally, the direct effects from MHL to HSI is (β = 0.452, 95%CI [0.304, 0.600], p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings provide empirical support for the roles of public stigma, self-stigma, and social support as mechanisms of behavioural change in MHL interventions. These factors increase HSI among elite athletes. Future studies should further test these mediating effects using experimental designs.
Keywords: Chinese elite athletes; help-seeking intention; mental health literacy; social support; stigma.
Copyright © 2024 Bu, Zhang, Liang, Han, Yi, Su and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Ajzen I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 50, 179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T - DOI
-
- Banjanovic E. S., Osborne J. W. (2016). Confidence intervals for effect sizes: applying bootstrap resampling. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 21:5. doi: 10.7275/dz3r-8n08 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

