Exploring the potential of myo-inositol in thyroid disease management: focus on thyroid cancer diagnosis and therapy
- PMID: 39329107
- PMCID: PMC11424451
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1418956
Exploring the potential of myo-inositol in thyroid disease management: focus on thyroid cancer diagnosis and therapy
Abstract
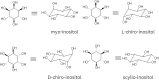
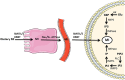
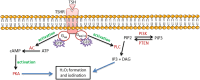
Thyroid cancer (TC) is a malignancy that is increasing in prevalence on a global scale, necessitating the development of innovative approaches for both diagnosis and treatment. Myo-inositol (MI) plays a crucial role in a wide range of physiological and pathological functions within human cells. To date, studies have investigated the function of MI in thyroid physiology as well as its potential therapeutic benefits for hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis. However, research in the field of TC is very restricted. Metabolomics studies have highlighted the promising diagnostic capabilities of MI, recognizing it as a metabolic biomarker for identifying thyroid tumors. Furthermore, MI can influence therapeutic characteristics by modulating key cellular pathways involved in TC. This review evaluates the potential application of MI as a naturally occurring compound in the management of thyroid diseases, including hypothyroidism, autoimmune thyroiditis, and especially TC. The limited number of studies conducted in the field of TC emphasizes the critical need for future research to comprehend the multifaceted role of MI in TC. A significant amount of research and clinical trials is necessary to understand the role of MI in the pathology of TC, its diagnostic and therapeutic potential, and to pave the way for personalized medicine strategies in managing this intricate disease.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer diagnosis; metabolomics; myoinositol; thyroid carcinoma; thyroid nodule.
Copyright © 2024 Razavi, Kalari, Haghzad, Haddadi, Nasiri and Hedayati.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of Inositol in Thyroid Physiology and in Subclinical Hypothyroidism Management.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 10;12:662582. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.662582. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34040582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myoinositol in Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 28;13:930756. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930756. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35837308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in metabolomics of thyroid cancer diagnosis and metabolic regulation.Endocrine. 2019 Jul;65(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-01904-1. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Endocrine. 2019. PMID: 30937722 Review.
-
The metabolomics and lipidomics window into thyroid cancer research.Biomarkers. 2017 Nov;22(7):595-603. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2016.1256429. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Biomarkers. 2017. PMID: 27805426
-
[Current questions of thyroid diseases in childhood].Orv Hetil. 2011 Apr 17;152(16):617-27. doi: 10.1556/OH.2011.29088. Orv Hetil. 2011. PMID: 21454178 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Development and characterization of a novel injectable thyroid extracellular matrix hydrogel for enhanced thyroid tissue engineering applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 27;12:1481295. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1481295. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39664883 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Potential of Metabolomics in Thyroid Cancer-A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;17(6):1017. doi: 10.3390/cancers17061017. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

