Identification of a histone deacetylase inhibitor as a therapeutic candidate for congenital central hypoventilation syndrome
- PMID: 39329148
- PMCID: PMC11426119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102319
Identification of a histone deacetylase inhibitor as a therapeutic candidate for congenital central hypoventilation syndrome
Abstract
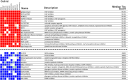
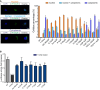
Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS), a rare genetic disease caused by heterozygous PHOX2B mutations, is characterized by life-threatening breathing deficiencies. PHOX2B is a transcription factor required for the specification of the autonomic nervous system, which contains, in particular, brainstem respiratory centers. In CCHS, PHOX2B mutations lead to cytoplasmic PHOX2B protein aggregations, thus compromising its transcriptional capability. Currently, the only available treatment for CCHS is assisted mechanical ventilation. Therefore, identifying molecules with alleviating effects on CCHS-related breathing impairments is of primary importance. A transcriptomic analysis of cells transfected with different PHOX2B constructs was used to identify compounds of interest with the CMap tool. Using fluorescence microscopy and luciferase assay, the selected molecules were further tested in vitro for their ability to restore the nuclear location and function of PHOX2B. Finally, an electrophysiological approach was used to investigate ex vivo the effects of the most promising molecule on respiratory activities of PHOX2B-mutant mouse isolated brainstem. The histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA was found to have low toxicity in vitro, to restore the proper location and function of PHOX2B protein, and to improve respiratory rhythm-related parameters ex vivo. Thus, our results identify SAHA as a promising agent to treat CCHS-associated breathing deficiencies.
Keywords: CCHS; MT: Bioinformatics; PHOX2B; aggregates; breathing; pharmacological treatment.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Weese-Mayer D.E., Silvestri J.M., Marazita M.L., Hoo J.J. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome: inheritance and relation to sudden infant death syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1993;47:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Pattyn A., Hirsch M., Goridis C., Brunet J.F. Control of hindbrain motor neuron differentiation by the homeobox gene Phox2b. Development. 2000;127:1349–1358. - PubMed
-
- Amiel J., Laudier B., Attié-Bitach T., Trang H., de Pontual L., Gener B., Trochet D., Etchevers H., Ray P., Simonneau M., et al. Polyalanine expansion and frameshift mutations of the paired-like homeobox gene PHOX2B in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:459–461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

