OSBPL10-CNBP axis mediates hypoxia-induced pancreatic cancer development
- PMID: 39329194
- PMCID: PMC11681314
- DOI: 10.1002/biof.2124
OSBPL10-CNBP axis mediates hypoxia-induced pancreatic cancer development
Abstract
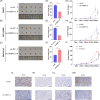
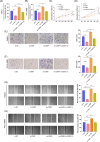
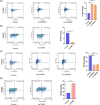
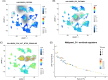
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of malignancies with worst outcomes among digestive system tumors. Identification of novel biomarkers is of great significance for treatment researches and prognosis prediction of pancreatic cancer patients. Due to OSBPL10 known involvement in oncogenic activity in other tumors, we elucidated the mechanism underlying its contribution to pancreatic cancer progression. We employed data from the Gene Expression Omnibus database to detect the expression of OSBPL10 in normal and pancreatic cancer tissues. A series of assays were conducted to assess the impact of OSBPL10 on the proliferation and metastatic capacities of pancreatic cancer cells and the influence of OSBPL10 on macrophages were evaluated by Flow cytometry. In addition, Co-immunoprecipitation, mass spectrometry, and western blot assays were utilized to investigate the potential mechanisms of OSBPL10 activity. From our study, OSBPL10 is revealed to be upregulated in pancreatic cancer, with poor prognosis. The overexpression promotes malignant behaviors of pancreatic cancer cells and has an impact on tumor immune microenvironment by stimulating the transformation M1 macrophages into M2 macrophages. Mechanistically, hypoxia induces the expression of OSBPL10 through interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α and the promoter region of OSBPL10. Additionally, OSBPL10 directly bound to CNBP, mediating CNBP expression and ultimately regulating the proliferation and metastasis capacity of pancreatic cancer cells, as well as influencing macrophage polarization. The research emphasized the oncogenic role of OSBPL10 in pancreatic cancer, uncovering key mechanisms involving hypoxia, HIF-1α, and CNBP. The finding suggests that OSBPL10 is a novel biomarker in pancreatic cancer, making it a potential therapeutic target for intervention in this malignancy.
Keywords: CNBP; OSBPL10; hypoxia; oncogene; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; tumor progression.
© 2024 The Author(s). BioFactors published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
SCF, regulated by HIF-1α, promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell progression.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0121338. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121338. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25799412 Free PMC article.
-
A potential signaling axis between RON kinase receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in pancreatic cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2021 Nov;60(11):734-745. doi: 10.1002/mc.23339. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Mol Carcinog. 2021. PMID: 34347914 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2020 Aug 1;484:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.04.018. Epub 2020 May 5. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32380129 Review.
-
A nicotine-induced positive feedback loop between HIF1A and YAP1 contributes to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 7;39(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01689-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32894161 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1) Recruits Macrophage to Activate Pancreatic Stellate Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 3;17(6):799. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060799. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27271610 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential prognostic biomarker of OSBPL10 in pan-cancer associated with immune infiltration.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 13. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03998-z. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40074843
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

