Foundation models in ophthalmology: opportunities and challenges
- PMID: 39329204
- PMCID: PMC11620320
- DOI: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000001091
Foundation models in ophthalmology: opportunities and challenges
Abstract
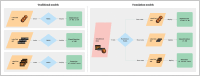
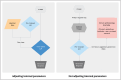
Purpose of review: Last year marked the development of the first foundation model in ophthalmology, RETFound, setting the stage for generalizable medical artificial intelligence (GMAI) that can adapt to novel tasks. Additionally, rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) technology, including models such as GPT-4 and Gemini, have been tailored for medical specialization and evaluated on clinical scenarios with promising results. This review explores the opportunities and challenges for further advancements in these technologies.
Recent findings: RETFound outperforms traditional deep learning models in specific tasks, even when only fine-tuned on small datasets. Additionally, LMMs like Med-Gemini and Medprompt GPT-4 perform better than out-of-the-box models for ophthalmology tasks. However, there is still a significant deficiency in ophthalmology-specific multimodal models. This gap is primarily due to the substantial computational resources required to train these models and the limitations of high-quality ophthalmology datasets.
Summary: Overall, foundation models in ophthalmology present promising opportunities but face challenges, particularly the need for high-quality, standardized datasets for training and specialization. Although development has primarily focused on large language and vision models, the greatest opportunities lie in advancing large multimodal models, which can more closely mimic the capabilities of clinicians.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Evaluating Bard Gemini Pro and GPT-4 Vision Against Student Performance in Medical Visual Question Answering: Comparative Case Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Dec 17;8:e57592. doi: 10.2196/57592. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 39714199 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Assessment of Corneal Endothelial Barrier Function Based on "Y-Junctions": A Finite Element Analysis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 May 1;66(5):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40408094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, et al. . Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med 2018; 24:1342–1350. - PubMed
-
- Bommasani R, Hudson DA, Adeli E, et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv [cs.LG]. 2021. Available at: http://arxiv.org/abs/2108.07258. [Accessed 3 June 2024]
-
- Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv [cs.CL]. 2020. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165. [Accessed 3 June 2024]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

